The apparel industry operates at the junction of creativity and utility acting upon consumer needs and wants. With rising demand worldwide and shifting regulations, ensuring textile quality and compliance has become paramount in this respect. Textile testing is the critical process of providing all necessary analytical insight a manufacturer or brand must have to get a garment that is durable, safe, and high-performing to market. The article elaborates on the importance of textile testing vis-a-vis quality assurance, regulatory compliance, and consumer trust. It will give readers an overview of how stringent testing maintains standards while promoting innovation, from understanding scientific testing techniques to looking at key compliance benchmarks.
Understanding Textile Testing
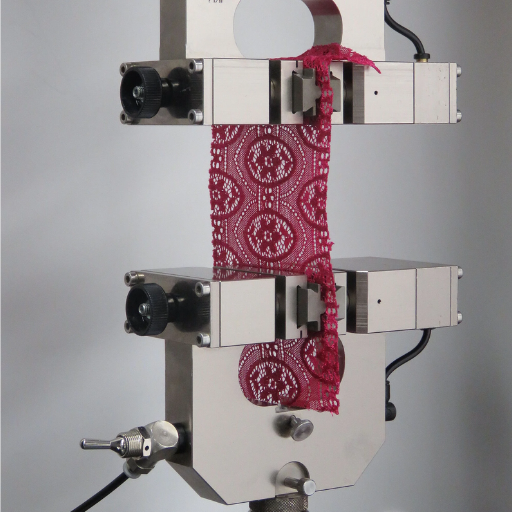
Textile testing is a systematic procedure that aims at evaluating the physical, chemical, and performance characteristics of textiles so as to qualify them for certain standards related to quality, safety, and regulations. Properties like strength, durability, color-fastness, flammability, water absorption, and moisture-wicking ability are tested for. These tests maintain consistency in product manufacture and assure adherence to specifications by laws, as well as expectation from the consumer. Standardized testing furnishes manufacturers with the possibility of identifying flaws so that a particular claim can be guaranteed or negated, or even translated into some new boiler terminology used in marketing.
What is Textile Testing?
Textile testing is a methodical and scientific process that analyzes the physical, mechanical, and chemical aspects of fabrics to establish their suitability for appointed applications and the standards set by the industry. Extremely important is the test, which verifies the performance, quality, and safety of a textile in varied environments and conditions. Recent data from Google’s search engine describe some of the more popular textile tests as tensile strength, abrasion resistance, pilling, and color-fastness tests. Furthermore, more advanced testing techniques now employ digital tools and AI to test for attributes like thermal conductivity, moisture manageability, and even the biodegradability of a sustainable fabric. Such extensive testing not only enables manufacturers to pass regulatory requirements but also paves the way for innovation concerning the development of high-performance, environmentally friendly textiles. Hence textile testing guarantees that the ultimate product will only stare back at its functional requirements and consumer expectations.
Importance of Textile Testing in Quality Assurance
Textile testing stays a life-blood of quality assurance with fabrics, ensuring that the fabric in question meets its function and lasts the required time in that function, ultimately affecting the textile product’s performance and consumer fulfillment. Textile tests are vital in verifying material properties such as tensile strength, color fastness, abrasion resistance, and dimensional stability. The test checks eliminate material failure cases and help with the smooth functioning of the supply chain; therefore, it increases compliance to international standards such as ISO, ASTM, and GOTS. The test will also innovate material design for advanced, sustainable, and high performance textiles based upon country-specific requirements-from apparel and homeacing to industrial and medical applications. Therefore, testing is a prerequisite to safeguarding the brand image, regulatory acceptance, and delivery of reliable products to the end-users.
Overview of Testing Solutions Available
Testing solutions, ranging from a relatively simple procedure to more complex and involved ones, are provided by the textile industries in a bid to meet various demands of quality, safety, and performance. Testing methods include the physical and mechanical tests: tensile strength, abrasion resistance, seam slippage tests guaranteeing durability, and product life. Chemical testing looks at colorfastness properties, pH levels, and pollutants, such as formaldehyde, thus fulfilling the environmental and safety regulations. The instrumentation for thermal and flammability tests is very high tech and can find some serious applications in automotive and gear for protective industries.
Moreover, microbiological and allergen testing is gaining prominence to ensure hygiene and consumer protection, especially within the area of healthcare and sports textiles. And then several laboratories provide specific testing services for the validation of certifications including OEKO-TEX® and GOTS, thereby troubleshooting for companies aiming for international eco-labels. These all-inclusive solutions allow manufacturers to harness their own materials’ properties and thereby apply them to market conditions and ensure regulatory framework.
Types of Textile Testing
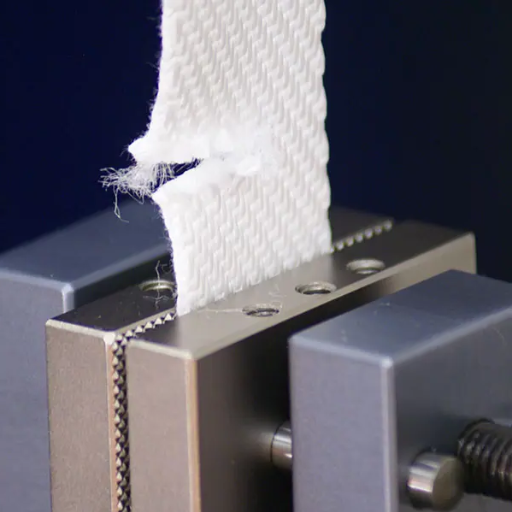
The types of textile testing include physical testing, chemical testing, performance testing, colorfastness testing, and ecological testing.
|
Test Type |
Key Points |
Parameters |
|---|---|---|
|
Physical Testing |
Strength, Density |
Tensile, GSM |
|
Chemical Testing |
Composition, pH |
Fiber ID, Acid |
|
Performance Testing |
Durability, Comfort |
Abrasion, Wick |
|
Colorfastness |
Wash, Light |
Fade, Bleed |
|
Ecological Testing |
Safety, Standards |
Toxins, Eco-cert |
Physical Testing Methods
Physical testing_methods are meant to assess the structural and mechanical nature of textiles and assure quality and performance. Usually attempted are:
1.Tensile Strength Test – The test measures the maximum strength that the fabric can absorb before breaking, thus determining its durability and load-bearing capability.
2.Rubbing of GSM – Grams per square meter (GSM) weigh a fabric, giving an indication of thickness for the end application.
3.Tear Strength Test – The resistance to tearing under specific circumstances is measured, and that is grasping for wear and tears.
4.Bursting Strength Test – This is predominantly for knit fabrics plasma where it measures the amount of force exerted on a fabric till it suddenly gives in under pressure.
Pilling Resistance Test – This test terminates the ability of the fabric to form pills that stain its surface quality in the long run.
Precision and reliability in the test results come from this giant equipment-type universal tensile tester, bursting tester, pilling tester, all of which are very instrumental in assessing textile quality.
Chemical Testing and Analysis
In textile industries, chemical testing is done to evaluate composition, properties, and performance of fabrics through chemical analysis. Testing may include identification of fiber content, durability testing for dye and finishes, and material testing for the presence of harmful substances. Most common testing methods include pH to check the acidity or alkalinity; quantitative analysis of fiber mixtures employing chemical solubility; and testing dyes for colorfastness to perspiration, washing, and light. Specific chemicals or contaminants are sometimes identified through analytical techniques such as FTIR and GC-MS to ensure their compliance with safety and environmental conditions. These methods provide relevant information with which manufacturers maintain quality standards and comply with regulations.
Mechanical Testing for Durability
Mechanical testing for durability pertains to verifying the ability of a material to withstand different types of stress and strain beyond a certain time. The common tests involve tensile strength testing, fatigue testing, and impact resistance testing. These methods represent real problems that could be faced in life to test the material’s performance through varied loads, forces, and environmental factors. Universal testing machines or impact testers may be engaged to measure the properties with high accuracy. Test results are reported in a laboratory environment, and as such, give somewhat useful parameters about material life expectancy, failure limit, and for industrial applications.
Key Standards and Certifications

Material performance is evaluated mainly through testing. Would standards and certifications enable testing inconsistencies, uncredentialed results, comparisons, and contradictions? Common frameworks include ASTM International standards, which offer detailed protocols of mechanical and impact testing of materials. International Organization for Standardization (ISO) certifications, like ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 17025 for testing laboratory competence, are also deemed essential benchmarks. Industry-specific codes and certifications one might require may include ASME standards for mechanical systems or IEC standards for materials used in electronic applications. On meeting these standards, their ability to establish the performance of materials becomes universally accepted, thus facilitating their application in specialized fields.
ISO Standards for Textile Testing
The ISO standards for textile testing are prepared for impartial standard setting, ensuring consistency, reliability, and reproducibility in the evaluation of textile materials with respect to their properties and performance. These standards are related to hundreds of testing procedures, namely tensile strength (ISO 13934-1), colorfastness (ISO 105 series), and dimensional stability of textiles (ISO 3759). We are thus able to test reliably for material properties while simultaneously conforming to the international standards hence taken across quality systems and global trade. Practicing the standards far exceeds the mere process of verifying, which guarantees that precise comparisons can be made to fulfill both regulatory and consumer requirements in the industry.
AATCC Testing Standards
The American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC) testing standards are widely accepted methods for the evaluation of the performance characteristics of textile materials. These standards test multiple areas of textile material properties, including those for color-fastness, moisture management, abrasion resistance, and antimicrobial activity. For example, AATCC TM61 tests for colorfastness to laundering, and AATCC TM22 tests for water-repellent properties in fabrics. Each method is developed by extensive industry collaborations to ensure their applicability in multiple textile applications. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers guarantee product reliability and customer satisfaction, as well as fulfill technical and regulatory requirements for the industry.
Compliance Testing and Regulations
Compliance testing is used to ensure that product performance, their established standards, regulations, or criteria are met against consumer safety, environment, and maintenance of access to market. REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) in the European Union, CPSIA (Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act) in the U.S., and ISO standards for chemical restriction, safety measuring methods, and quality assurance supply testing requirements. They measure the physical properties, chemical composition of the product, and environmental impacts to comply with those regulations.
Global bodies producing standardized test methods—such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) and AATCC (American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists)—are widely accepted in various industries. Certification bodies involved in compliance testing, such as OEKO-TEX certificates for textiles, help facilitate international trade and consumer confidence by certifying that products conform to stringent safety and quality requirements. The entire framework wrapped by these regulations attempts at standardization so manufacturers can at least operate within agreed technical, legal, and ecological specifications.
Textile Testing Equipment and Laboratories
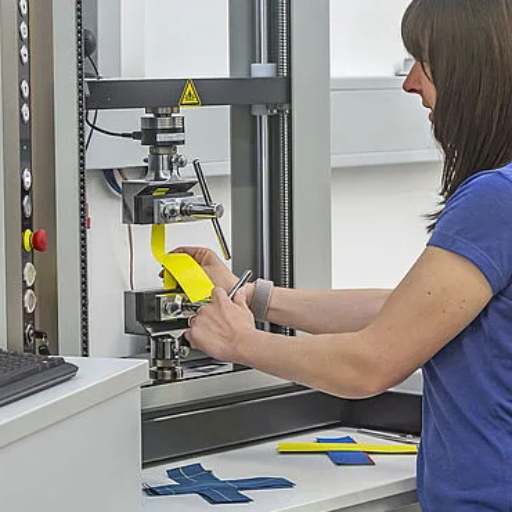

Testing equipment and laboratories in the textile field are a vital component that ensures the conformity of materials and products to established performance, safety, and quality standards. Such equipment would be tensile testing machines for strength testing, spectrophotometers for color testing, abrasion testers for wear testing, and moisture testers for hygroscopicity. Laboratories that are specifically equipped have facilities for carrying out these tests under controlled environments according to internationally recognized test methods such as ASTM, ISO, and AATCC standards. These testing facilities and laboratories, with the help of their precision instruments and methodologies, help manufacturers identify materials that do not conform, help in designing products better, help in reducing defects, and finally comply with the regulations of a particular country, industry, or market.
Overview of Testing Laboratories
The testing laboratories are majorly involved with the activities of quality and testing with respect to the materials, products, and systems, covering a large area of safety and performance. They are high-tech establishments with stringent protocols for performing tests related to the health sector, construction, textiles, electronics, and more. All renowned testing laboratories strive to maintain adherence to global standards of ISO/IEC 17025 to classify their results as valid and reliable. The general testing services rendered by them include mechanical, chemical, and environmental testing, furnishing data that are intended to be put to use in the manufacturing process, regulatory compliance, and innovation. The knowledge secured from the testing laboratories helps the stakeholders to diminish risks and guarantee sustainability in the manufacturing and operation processes.
Advanced Testing Equipment Used
We keep putting on use the most advanced testing equipment to realize timely, accurate, and reliable experimental results for our analyses. It includes universal testing machines for mechanical properties, gas chromatographs and mass spectrometers for chemical analyses, and environmental chambers for conducting extremely rigorous tests. We also heavily rely on advanced microscopy facilities, namely SEMs, technical platforms able to characterize materials at nano and micro scales. Our advanced equipment arsenal allows us to conform to the stringent standards and address more industries in their quest for quality and performance.
Global Testing Laboratories and Their Roles
Global testing laboratories play a pivotal role in fixing product reliability, safety, and international standards compliance. Among the services rendered by global testing laboratories are material testing, environmental simulation, failure analysis, and performance verification. Laboratories ensure that the products comply with regulations such as ISO, ASTM, and standards of other organizations recognized worldwide, which is very important for gaining market access and consumer confidence. Additionally, their novel technologies in material identification, spectroscopy, thermal analysis, and nondestructive testing lay a risk-bottoming platform that aerospace, automotive, electronics, and construction industries take advantage of, to lift product durability. Simulating extreme environmental conditions to identify design vulnerabilities fosters innovation among manufacturers on a high scale of quality and safety. They also extend toward the project’s global supply chains through verification of raw material integrity and harmonize standards globally, thereby building trust and enhancing efficiency across industries.
The Role of Textile Testing in the Supply Chain

Textile testing is positioned at the center stage of managing quality factors, compliance, and performance within the series of chain events. Testing involves procedures to determine fiber strength, durability, color fastness, and chemical composition in textiles, certifying their conformity to industry standards and regulations. Defects are found at an early stage through testing, thereby mitigating waste and developing consumer confidence. Furthermore, testing helps the environment by confirming the adoption of greener materials and processes, thus creating a more effective and transparent supply chain.
Impact on Manufacturing and Production
Textile testing and quality control directly impact manufacturing and production, improved further as textile testing quality control practices become increasingly standardized. Production problems can be identified and rectified through testing methods in order to limit periods of downtime and losses due to scrap. Likewise, product consistency is retained through testing, which lowers rejection and expense caused by faulty material. Also, testing aids in the introduction of novel approaches, such as the latest fiber blends or the latest sustainable technologies, into production processes and activities in a timely manner. Thus, it assures greater reliability and efficiency in manufacturing processes in line with the standards laid down by the industry and accepted by the purchasing public.
Ensuring Product Performance and Safety
Product performance and safety are literally the packing of each production arsenal of a heavy testing protocol and the continuous adherence to set quality assurance standards. Testing methods are based predominantly on such procedures as tensile strength measuring or thermal and pressure analyses followed by flammability tests to a good firmness of the tested material and its performance through various conditions on functions. Using these methods must follow certain internationally accepted standards such as ISO or ASTM or the ODHA for consideration of product safety and consumer protection.
Real-time monitoring shall assure safety by identifying deviations. Incorporation of traceability starts to improve safety as well. Coupled with risk management practices such as FMEA and Hazard Identification, this will ensure that safety issues have been adequately addressed before the products are released to the market. Having strong testing protocols paired with good safety measures will put the manufacturer in a position to offer the market perfectly performing, safe, and reliable products expected by customers and regulatory authorities.
Building Consumer Trust through Testing
Consumer trust builds on thorough product-testing techniques. I guard the process of testing to ensure safety, performance, and compliance with industry standards of each product. If and when any defect like functionality or stress failures appears, this is discussed in detail, thus giving rise to some level of trust before the customer even receives the product. I maintain this trust throughout by fully sharing testing result reports with all parties and recommend. Open communication on risk resolution leads to customer loyalty.
Reference Sources
-
Quality Assurance in the Apparel Industry – This article reviews quality control and assurance in the apparel industry, highlighting key challenges faced by fashion brands.
-
Quality Control in the Textile Industry – Discusses standardized testing methods like seam strength, tear resistance, and shrinkage to validate garment quality.
-
Textile Testing – Explores the significance of textile testing and its role in ensuring product quality and safety.
-
Apparel Testing and Quality Control | A Smarter Sourcing Guide – Provides insights into how apparel testing and quality control strengthen product quality and ensure high standards.
-
Quality Testing – Focuses on reliable and consistent testing methods, including proper product sampling and working with independent testing labs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q:What is textile testing and why is it important for fabric quality?
A:Textile testing refers to the evaluation of the properties and performance of textile products, including yarn, fabrics, and fibers. It is important insofar as to meet safety regulations and quality standards so the consumer gets valid textile and apparel products. A good testing procedure will identify points in the fabric where weaknesses exist, which may cause failures in the finished product.
Q:What are some common types of fabric tests done in the apparel industry?
A:Some of the types of fabric testing common in the apparel industry are physical and chemical tests for tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and colorfastness. Martindale testing measures the strength of the fabric while fiber testing methods are used to analyze the composition and quality of yarns and fibers in textile manufacture.
Q:How does yarn testing affect the quality of textile product?
A:Yarn testing is used to determine the strength, uniformity, and overall quality of yarns used for textile products. By studying the characteristics of the yarn, the manufacturers can ensure that the product meets performance standards for durability and that the fabric is of a higher quality.
Q:What is the role of testing laboratories in textile and leather testing?
A:Testing laboratories offer services useful to manufacturers to ascertain the quality and safety of textile and leather materials. They carry out various standardized tests, like those from the American Society for Testing and Materials, which include resistance to pilling and resistance to thermal conditions, so that they comply with the regulations and standards set forth for the textile and leather industry.
Q:What is the Martindale test? Describe the relationship between the Martindale test and fabric testing.
A:Martindale is a particular method to test the abrasion resistance of acoustic textile fabrics. A controlled rubbing action is imparted to the fabric, which therefore has to pass through a test for wear and tear resistance- an important medium for evaluating the longevity and the durability of apparel and related products.
Q:What are the safety regulations under textile testing for children’s sleepwear?
A:Safety regulations give rise to testing of children’s sleepwear to prove that the materials employed are flame resistant and are not hazardous to the children. It is therefore compulsory that such regulations are abided by, and labs undertake the testing to certify fabrics utilized in children’s sleepwear as conforming to safety standards prescribed by bodies such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Q:How do testing services assist textile manufacturers in meeting their testing requirements?
A:Textile testing services offer a complete array of services whereby manufacturers can be helped to meet their testing requirements. By analyzing the properties of fabrics and yarns from beginning to end, this service helps ensure that textile products meet these standards on a worldwide basis, thereby producing better quality and efficiency that satisfy the consumer.
Q:What significance does fiber testing hold in textile production?
A:Fiber testing holds significance in textile production as it determines the quality and characteristics of the raw materials. When a manufacturer understands the composition and property of fibers, he can choose for his products the proper types of fabric that furnish the best performance, durability, and comfort to his finished textile products.






