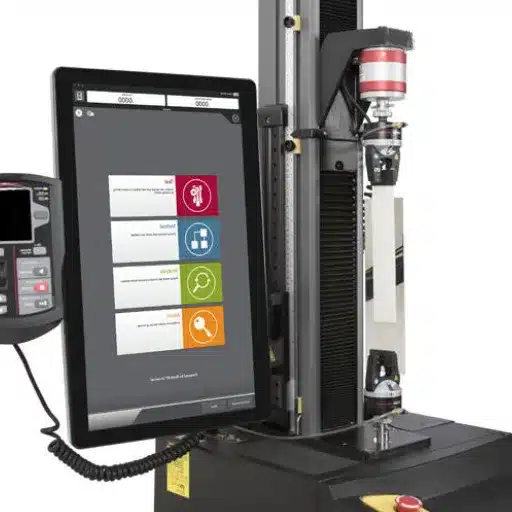
Wood is undoubtedly the most readily available natural material which supports a lot of diverse industries from construction of buildings to making furniture. However, for all its different uses, it is of paramount importance to test the products thoroughly and conform to the standards in order to certify their quality, safety and longevity. In this context, the purpose of this blog is to discuss the essentiality of wood testing and product evaluation in products and how they sustain the standards of the industry while at the same time the consumer is protected. There would be a discussion of the different approaches of measuring properties of wood, significance of adherence to standards and regulations, and ways through which product quality tests help in minimizing the negative impact to product life and usage. Manufacturers, suppliers and consumers need to understand these methods in order to maintain the quality of wood works amidst the growing and challenging market.
Understanding Wood Testing
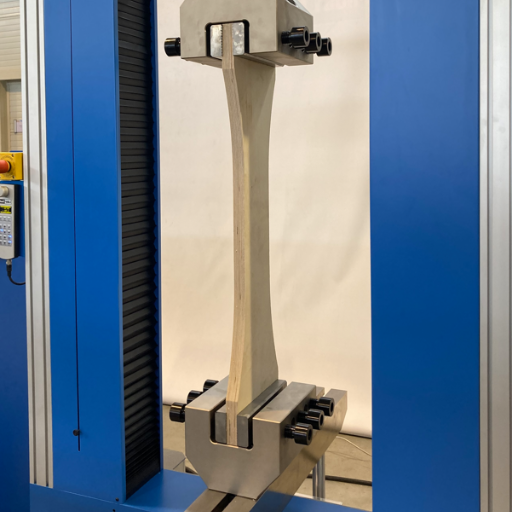

Let’s start with explaining what wood-testing means. This is a term used to describe the procedures designed to assess the wood’s structure, physical, mechanical, as well as chemical properties for the purposes of investigating its quality, performance and fitness for use. This normally comprises looking into the content of its density, its moisture, how much force it takes to break it and other physical and biological factors that would or would not allow degradation or any other type of attack. It is important to test the wood to make sure it conforms to the necessary performance standards and does not jeopardize the safety, longevity or sustainability of the product being constructed, produced or otherwise employed.
Importance of Wood Testing
Ensuring that the material’s structural integrity, safety and performance do not falter with time is a key purpose of wood products testing. By determining mechanical strength, moisture content, resistance to biological agents and even decay due to the environment, it becomes possible to foresee how this wood material will behave in particular conditions. This is especially important in the construction industry where wood is required to comply with load and durable requirements.
In addition, wood testing reinforces the efforts for sustainable development, or sustainable production primarily through the identification of defects, efficient use of resources and lastly by the minimization of waste. For the manufacturers, it guarantees the reliability and also meets the fundamental certifications such as ASTM or ISO. Valid test methods destructive or non-destructive in nature contain voluminous data that helps in deciding material usage, quality control and conformity to standards. When stringent testing measures are not in place, chances of collapse are higher, which may mean structural insecurity and increased costs.
Key Types of Wood Products
Key types of wood products include solid wood, engineered wood, plywood, veneer, particleboard, MDF (medium-density fiberboard), OSB (oriented strand board), and laminated wood.
|
Wood Type |
Features |
Common Uses |
Advantages |
Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Solid Wood |
Natural, durable |
Furniture, floors |
Strength |
Expensive |
|
Engineered |
Layered, stable |
Flooring, beams |
Uniformity |
Limited grain |
|
Plywood |
Veneer layers |
Cabinets, roofs |
Strong, light |
Not moisture-proof |
|
Veneer |
Thin wood sheet |
Panels, doors |
Aesthetic |
Fragile |
|
Particleboard |
Compressed chips |
Shelves, panels |
Cost-effective |
Low durability |
|
MDF |
Fine fiberboard |
Cabinets, doors |
Smooth surface |
Heavy |
|
OSB |
Stranded layers |
Sheathing, walls |
Strong bond |
Rough texture |
|
Laminated |
Bonded layers |
Furniture, beams |
Customizable |
Adhesive usage |
Overview of Testing Applications
Testing applications for engineered wood products typically focuses on evaluating their structural performance, durability, and usability in various environments. Strength tests measure load-bearing capacity and resistance to bending or compression, critical for applications like flooring or beams. Moisture resistance testing assesses performance under humid conditions, particularly for materials like plywood or OSB that may not inherently resist water. Surface quality analysis is crucial for veneers and MDF, ensuring smoothness and finish compatibility for aesthetic uses. Additionally, adhesive bond strength tests determine the layers’ integrity in laminated and particleboard products, vital for long-term reliability. Comprehensive testing ensures these materials meet industry standards and application-specific requirements.
Testing Methods for Wood Products
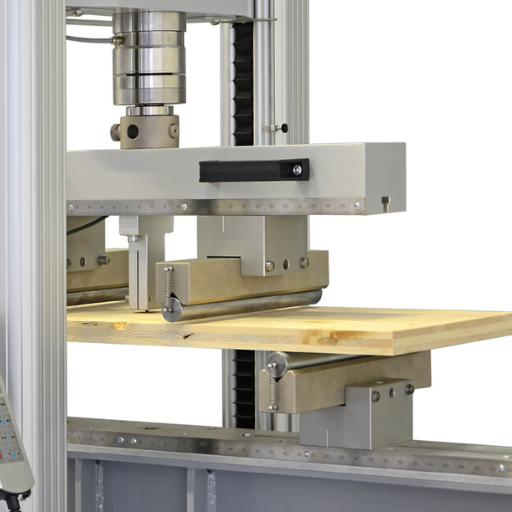

Common testing methods for wood products include mechanical testing, moisture content analysis, fire resistance testing, chemical treatment evaluation, and durability assessment.
|
Test Type |
Purpose |
Key Standard |
Measured Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Mechanical Testing |
Assess strength |
ASTM D143 |
Strength, Elasticity |
|
Moisture Analysis |
Determine moisture |
ASTM D4442 |
Moisture %, Stability |
|
Fire Resistance Test |
Fire safety check |
ASTM E84 |
Ignition, Flame Spread |
|
Chemical Evaluation |
Check treatments |
AWPA Standards |
Preservative Content |
|
Durability Test |
Longevity testing |
ISO 15686 |
Resistance to Decay |
Compression Testing Techniques
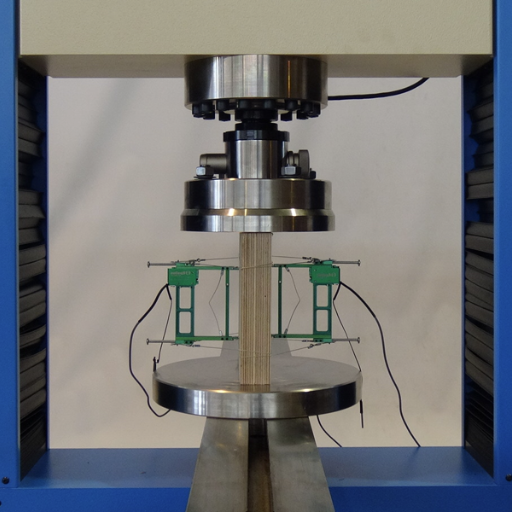
Compression testing involves examining materials in the direction opposite to tensile forces, i.e., to subject them to loads. It is a process of force application on a material sample during which the properties measured are compressive strength, stiffness to a degree, or how the sample deforms with an increase in load. Usually, this is done by using a universal testing machine (for example, that of the commonly used ASTM E9), which is a standard practice worldwide for such testing procedures to be followed. It frequently necessitates the use of standard samples, whether cylindrical, cuboidal, or prismatic specimens are prepared to enable uniform application of the load.
Compression or squeeze test modern approaches involve high precision sensors and software in instrumentation which renders data to the researchers on site and indicates the zones of stress levels and danger in the structures. Such testing is used by industries when they deal with metals, plastics, polymer systems, metalcomposites to give reasons for safety and performance of such materials in reference to standards set by the regulatory bodies.
Shear Testing Procedures
Shear testing is a common procedure that is performed to assess the shear strength, modulus, and behavior of materials subjected to shear forces (forces in anti-parallel direction acting along the two planes of the solid). It generally involves cutting the samples to satisfy specific dimensions to avoid bias and variability. Single-shear, double-shear, and punch shear configurations can be employed depending on the material and the industry requirements. High-tech equipment such as universal testing machines fitted with shear testing attachments ensures that forces are applied correctly and in the right doses.
It is important to emphasize that during the measurements, the sample is attached to a frame and the deformations are monitored continuously. Also, in order to obtain reliable results, the rate of loading, orientation of the specimen, and the environments have to be kept in check. Every engineering field, from aeronautics to constructions utilizes shear testing to evaluate the shear phenomena of a component such as in a joint or a surface for endurance against overlong slipping.
Moisture Content Analysis
Moisture content analysis involves the determination of the mass of water contained within a given sample of a material, as a fraction in percentage of the sample’s mass. This measurement is important in a range of sectors including food, agriculture, medicinal and building industries, since presence of moisture affects the quality and durability of products to a very high degree. Moisture determination is carried out by gravimetric techniques, which includes oven drying, wherein the loss in weight is measured after drying, or it can also be performed using sophisticated instruments such as Karl Fischer Titration or near Infrared Spectroscopy to achieve the results quickly and accurately. Correct analysis of moisture content controls the production quality and protection from spoilage and collapse of foods and materials up to the standards required by the specific industry highlighting the inherent value of the procedure in all related fields including wood products testing and structural material examination.
Industry Standards and Certifications

Following standard operating procedures, moisture content measurement procedures must be carried out within recognized parameter limits. Among the key parameters here are below the ISO 12570, which deals with the moisture content of building materials and the ASTM D2216 on soil, and that of foods and agricultural commodities as specified by the AOAC. Adherence to such standards ensures that the procedure principles used for such purposes perform accurately and repetitively. In addition, obtaining accreditation, should include such standards as ISO 9000, for quality system certification, adds value to the testing processes by making them comparable with the international standards.
ASTM Standards for Wood Testing
The ASTM standards for testing the wood products encompass broad-based protocols that seek to assess the mechanical, physical, as well as chemical attributes of wood and wood derivatives. Noteworthy standards are ASTM D143, which describes the procedures for testing various mechanical properties such as tension, compression, and shear in both small clear specimens and structural sized components. Further attention has been paid towards standards D198, which covers procedures for testing full-size structural lumber and glued laminated timber focusing on bending, torsion and joint strength. Finally, ASTM D4442 focuses on accurate measurement of moisture content in wood products by oven-drying, and by rapid moisture content testing. With these standards in place, inaccurate, unreliable and non-comparable test results are eliminated, thereby achieving uniformity during research, quality control and regulation/enforcement.
ISO Certifications and Their Importance
ISO certification signifies the recognition and adherence to accepted international norms on products, services or systems particularly in respect of quality, safety and efficiency. These, again are mandatory certifications issued by the International Standard Organization (ISO) and are very important in assuring compliance to best and regulatory practices. Among them are ISO 9001 which involves the standards of the system of quality management, ISO 14001 for systems of environmental management and ISO 27001 for systems of information security management.
ISO certifications are important because they reinforce the credibility of an organization, improve its performance and increase its customers’ confidence. By following specific standards and improvement cycles, the management will achieve the result where there will be low level of occurrence of mistakes and less risky operation as well as ensured effectiveness of performance. Also, as global practice, engagement in cross-border business relations is encouraged when certificates are in place, that is, many investors or business partners compel adherence to certain certification before a partnership is formed or a purchase is made promoting competence and assurance among shareholders.
Impact on Testing Practices
In my understanding, imbibing these certifications into the system, raises testing practices to a high level because it provides a framework to use handled methodologies including industry standard practices. This assures that every testing activity is performed in a more orderly manner and more importantly, specified standards are always replicated in all the practices, thus reducing potential flaws and challenges. Moreover, certifications promote also risk-based techniques towards the conduct of testing thereby optimizing the focus of the team on the more important facets of testing. Consequently, it creates assurance to the stakeholders as it assures that the testing results meet the required standards both in the eyes of the regulatory authorities as well as the induced customer level enhancing the quality and dependability of the tested products.’
Advancements in Wood Testing Technology
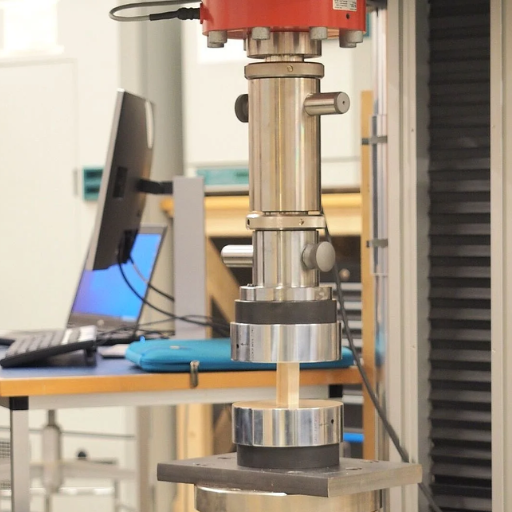

There have been immense improvements in the realm of wood products testing technologies which have enhanced the precision, convenience, and range of tests on the materials. Non-destructive testing or NDT techniques such as the application of ultrasound or X-rays imaging have solved the issue of internal defects off the given wood without disturbing the material. Moreover, integrated systems that take the power of machine learning can measure the parameters of wood such as wood density, moisture content, or even mechanical properties – to a remarkable degree. These developments help to better assess the probabilistic model of the behavior of wooden elements in natural and operational acts, thus benefitting also the control in the implementation of standards. Finally, there is also development regarding the testing units that have more capabilities for down travels resulting in lesser turnaround times as well as logistics costs. All of these one way or the other through these advances have precision management of resources and more importantly environmentally friendly activities and improved wood and wood products performance.
Use of Automated Testing Systems
Automatic testing systems have been implemented in the wood industry and have ensured outputs of tests due to integration of complex technologies such as robotic machine vision and algorithmic based technology. These systems are capable of quickly measuring the various features such as strength, moisture content and even structure with very little human input. The current development comes with non-destructive testing systems which involve analysing internal and external structures of wood using measuring instruments and cameras for precision and reproducibility. Automation further streamlines the production processes by incorporating quality management within the assembly line for faster decision making and reduction of material wastage. Use of these automated testing systems, therefore enhances the practice efficiency, increases product safety and is utilized in sectors that have rigorous regulatory safety standards.
AI and Digital Tools in Testing
Testing is going through a makeover with the help of Artificial Intelligence and digital solutions which have enhanced the effectiveness, speed and extent of the methodologies. In predictive analysis defect or inconsistency detection has been a primary focus where machine learning algorithms have eliminated most of the labor. Inclusion of Artificial Intelligence capabilities in digital platforms helps in the organization and application of large datasets, such that outcomes are generated and patterns detected to avoid issues. A new technological advancement includes cloud based testing tools that helps teams to test remotely to allow the system to work efficiently even in different environments.
In addition, the testing process has been drastically shortened by the introduction of automation which uses artificial intelligence technology, ruling out the possibility of errors which were inevitable with human beings. For example with the help of digital vision analysis driven by AI, the defect or quality can be checked with the greatest precision which is especially relevant to the complex systems such as manufacturing processes or software. Digital twin technology supported by artificial intelligence allows simulators to be created for products or systems thus different possibilities can be tried out without the physical resources. The above two incorporate the needs of almost all modern processes: compliance, high-quality, cost-saving, leading to higher sustainability of modernization.
Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency
The expectation of improving effectiveness, accuracy, and efficiency in different sectors, through the use of technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation tools are being realized. Each problem is correctly addressed by the use of AI powered data analytics capabilities which allow real time pattern and anomaly detection enabling timely decisions. Process improvement is achieved by the use of machine learning models which are able to train themselves on the datasets provided over a period of time optimizing the systems at play and reducing any errors that may arise. Redundant work can also be automated to produce consistent results without the need for human intervention and resources may be demobilized elsewhere. All these technologies come together to help increase performance accuracy, avoid unnecessary wastage of resources and very importantly they work hand in hand with improving output greatly.
Quality Assurance and Safety in Wood Products
Any quality assurance process in wood products testing tries to ensure that specific materials used comply with strength, resistance-destructive to environmental facts like moisture or pest and durability in shape. The most common as well as most sophisticated types of such tests include moisture content, mechanical performance test to mention a few for checking with the specifications. On the other hand, safety seeks to reduce risks such as fire, structural collapse and exposure to toxic substances like formaldehyde. Conservation as per standards such as ASTM or production according to for example FSC certification are safety and sustainability measures to the products.
Role of Testing in Quality Assurance
Testing is essential to ensure the quality of products within which they are required to optimize performance at the level of specified conditions. It promotes early identification of defects in the production thereof, averting expensive mistakes and ensuring adherence with statutory and industrial requirements. The functionality of a product, its performance and its durability are some of the key parameters evaluated while employing such tests. Sophisticated methods such as non-destructive tests (NDT) aimed at resolving interrelation between materials and structures are now widely adopted in quality control for some purposes. By ensuring effectual laws and standards examination is applied each time, this helps the enterprise in quality and safety research and also saves the customers from enhancing risks.
Importance of Testing for Treated Wood
The consideration of issues related to testing of treated woods is vital mainly because ensuring their performance level and compliance in different environments especially those where the structural safety is high is very important. Most of the time, treated wood is subject to extreme stresses including moisture, pest attack and direct UV onslaught, therefore it has to be evaluated properly. One of the main protocols in place is penetration and retention which assesses the penetration depths and concentration of wood treatment materials to changes from metabolism and microbes. Other tests will target mechanical characteristics like strength and durability to certify wood for particular applications. Those more elaborate as accelerated climatic ageing and changes due to a decay fungus give long-term perspectives. Therefore, it is possible for manufacturers to guarantee the quality of products, perform the necessary compliance procedures and even help in promoting consumer confidence levels in the use of treated wood products because of the above-mentioned tests.
Case Studies: Testing in Various Industries
Testing across industries includes applications in construction, furniture manufacturing, marine environments, and residential decking.
|
Industry |
Tests Conducted |
Purpose |
Key Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Construction |
Strength, durability |
Structural safety |
Load test |
|
Furniture Manufacturing |
Surface finish, adhesion |
Aesthetic appeal |
Finish quality |
|
Marine Environments |
Fungal decay, moisture |
Resistance to water |
Decay rating |
|
Residential Decking |
Weathering, UV testing |
Longevity in use |
UV stability |
Reference Sources
-
T,C&A Lab – Wood Testing Services: A professional third-party testing organization providing wood testing services according to ISO and ASTM standards.
-
TestResources – Wood & Wood Products Testing: Offers universal test machines and solutions for wood and wood product testing.
-
Deskera – Ensuring Quality Control in Wood Production: Discusses quality control measures like inspections, testing, and sampling in wood production.
-
Deskera – Best Practices for Wood Manufacturing Quality Control: Covers testing and certification practices to meet required standards in wood manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Which procedures are accepted as the norm in the area of Wood Products Testing?
A: The standard test methods for wood products testing consist in common practices that are usually invoked to control quality and performance of wood and wood-based materials, depending on the purpose. There are tests for different physical properties, most commonly strength and durability, as well as others offered for decay. Also, typical examinations are performed such as specific gravity measurement, determination of flexural strength, and moisture content. All these tests are useful for assessing the potential usage of the wood for various purposes for example structural wood products, prefabricated wood i-joist, among others.
Q: Do adhesives enhance the performance of timber and if so, how?
A: Timber performance is enhanced by bonding several wood woods together with an adhesive to enhance the composite materials, especially in the glue laminated and structural panels. Varying adhesives come with varying strengths, stiffnesses and wet ability that affect the performance of the adhesive(a)s material. This means that wood adhesives must be tested to serve their purpose and also meet standards of specific use, especially where there is fungus liable decay.
Q: How is specific gravity relevant in testing of woods?
A: Specific gravity is important in the study of woods because it describes the density and strength of different species of wood. It excises the ultimate strength, retention and culpability of wood products. Most strong timber species have high specific gravity which influences the improving use of wood products including the subject. In practical aspects, specific gravity testing is essential in aiding in the identification process and subsequent assessment of materials.
Q: What crowning agents for wood are available and what are the procedures for analyzing them?
A: Common wood preservatives are chemical substances applied to the wood to stop the wood from rotting, insects or from weather conditions. Both laboratory soil-block culture and accelerated laboratory tests to study the effectiveness of preservative systems are among the most common performance testing procedures of wood preservatives. The results of these experiments help in understanding how preservatives can elongate the service life of products made from wood, such as wood utility poles and wood paneling among others.
Q: Describe the role of laboratory tests in enhancing the performance of wood structural materials?
A: Laboratory tests play a significant ex in building wood structural products since Research and Development activities relating to any given product or product enhancements include testing on wood structural products. Such include flexural strength/durability/decay test parameters, but through the standardized test methods. The insight brought by the laboratory testing helps in enhancing the performance of the products and help manufacturers to determine how useful the products are in terms of safety and standard.
Q. How does moisture content affect work with wood products?
A: The moisture content of wood products greatly affects their performance. It alters the strength, retentive capacity and rot proofing of any material. Testing moisture content in wood becomes very important since high moisture content can cause warping, and splitting and cause a poor augging distance. Ability to manage moisture content is core in choosing wood and assured maintenance of wood used in different anxieties.
Q: What is the purpose of decay testing in relation to the assessment of products made from wood?
A: Decay testing involves the monitoring of the decay resistance capacity of wood against biotic agents such as fungi and insects. It entails subjecting wood samples to deterioration favorable conditions and testing their response. That will target wood preservation methods and also the expected life span of the wood in such challenging environments.
Q: How do structural wood and wood-based products undergo quality checks?
A: Testing of quality in structural wood and wood-based products is done through various standardized tests to measure mechanical properties, durability and environmental resistance. The tests consist of flexural testing, specific gravity, and moisture content testing to name a few. Offices, overhangers and roof frames made from timber structural panels and prefabricated timber I-joists are some of the examples which ensure that.
Q What are some of the pros of using glulam in buildings?
A: Glulam which is glued laminated timber has very many benefits in the construction industry among them is high weight to strength ratio, ability to form in different ways and most importantly the warping of the product . Glulam is fabricated through the laminations of timber held together by very tough bonding chemicals for building members such as great span spaces. To ensure that a sufficient utilization of glulam towards beam work, column erection and other structural members is appropriate, the gathered data and especially the structural performance meeting the requirements is parameterized in terms of adequacy.






