Being a critical test in adhesive testing, peel testing finds great applications across industries for measuring bond strength between two components. It tests an adhesive’s performance under certain environments, giving manufacturers and engineers very useful data. Peel strength testing is essential for ensuring that a medical device will perform as expected; it establishes that automotive parts will endure and that packaging materials will be tested to peel, seal, and package. Hence, product quality versus performance standards are dependent on understanding peel strength. The article addresses the basics of peel testing, discusses the application of the test, and delves into why a truly successful measurement of peel strength is fundamental for reliable and consistent adhesive performance.
Introduction to Peel Testing
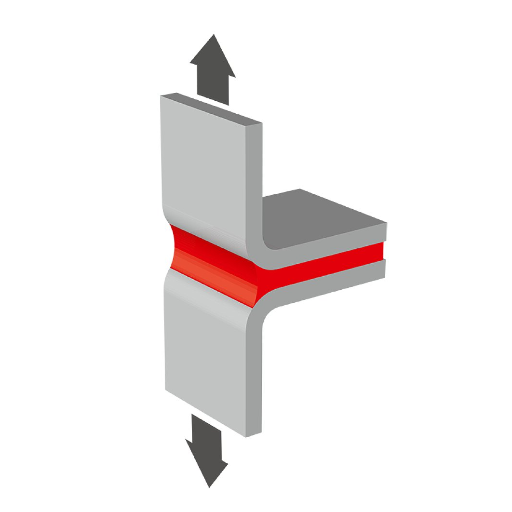
Peel testing is a method that measures adhesive strength or bonding performance between two materials. It gives us a controlled force application to pelt two bonded layers apart while determining durability and reliability of the adhesive under select circumstances. This test has wide applications in industries such as manufacturing, automobile, and medical, where it is extremely dependent on strong adhesive bonding for product functioning.
What is a Peel Test?
A peel test mechanical testing method is applied to evaluate the adhesive bond strength between two materials with a tensile force applied at a certain angle, usually 90 to 180 degrees. From an experimental viewpoint, the force required to progressively separate one material from another is determined; that is very relevant in establishing the integrity and durability of adhesion bonds given a specified set of conditions. Recent trade views acknowledge that peel testing remains a crucial aspect of quality control, especially in high-value and critical applications such as aerospace and electronics, where bonding requires very precise bonding techniques. The latest technology developments in peel testing emphasize automation and high-resolution force measurement methodology to make sure they yield valid and reproducible results.
Importance of Peel Strength in Material Evaluation
Peel strength is of utmost importance in material evaluation because it speaks directly about the reliability and ability of adhesive bonds to perform. Of what I researched, peel strength is very relevant to determine how well adhesive joints withstand strength, pressure, and bending forces during peeling. The sources keep underscoring that high peel strength means solid bonding, especially vital in critical industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. It provides safety and ensures durability of products where the failure of adhesive bonds might result in serious implications. On the other hand, another major development in these testing procedures is that the measurements are taking a step forward toward more accuracy and repeatability, which ease material identification and process optimization.
Overview of ASTM D1876 Standards
The ASTM D1876 standard, commonly called the “Peel Resistance of Adhesives (T-Peel Test)” method, determines the peel strength of adhesive bonds. It is mainly used for flexible materials where the force needed to peel two bonded substrates apart is measured at a constant rate of separation. Controlled environments are maintained during testing for temperature, speed, and sample-preparation conditions. ASTM D1876 is an appropriate test for definitive, comparative examinations to assess the strength characteristics of adhesive bonds for durability, wear-resistance, and ageing qualities in various industries, assisting in activities associated with material specification and quality control of manufacturing processes.
Types of Peel Tests
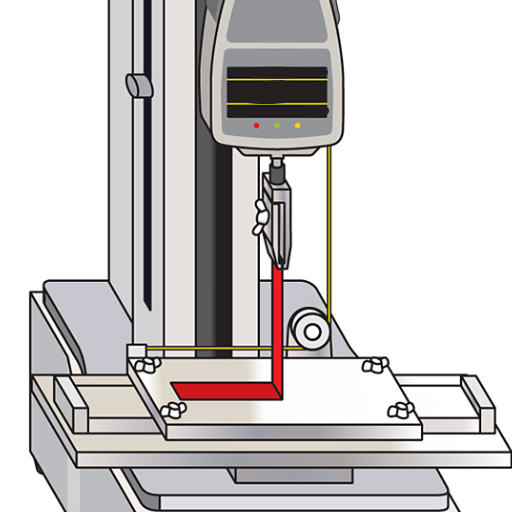
Peel tests are commonly categorized into T-peel, 90-degree peel, 180-degree peel, climbing drum peel, and floating roller peel.
|
Test Type |
Angle |
Purpose |
Key Uses |
Force Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
T-Peel |
180° |
Bond strength |
Adhesives |
Tensile |
|
90-Degree Peel |
90° |
Bond integrity |
Films, tapes |
Peel force |
|
180-Degree Peel |
180° |
Adhesion |
Laminates |
Separation |
|
Climbing Drum |
Variable |
Bond uniformity |
Composites |
Continuous |
|
Floating Roller |
Variable |
Flex testing |
Flexible mats |
Rolling force |
90-Degree Peel Test
The 90-Degree Peel Test is a standardized method to assess the adhesion strength between materials, especially with flexible substrates attached to rigid surfaces. In this test, one material is peeled from another at a fixed 90-degree angle, while the peel force is recorded. Typically, the test employs a tensile testing machine that maintains a constant peel speed while recording the force. This test finds many applications with tapes, films, labels, and any adhesive product where bond integrity is paramount. The test essentially sets a numerical value used in analyzing the reliability and performance of adhesive systems under given conditions.
180-Degree Peel Test
The 180-Degree Peel Test is one of the more traditional methods used for evaluating the adhesion strength of flexible materials bonded to rigid or flexible substrates. In a 180-Degree Peel Test, a flexible specimen, such as tape, film, or laminate, is peeled from the substrate at a controlled speed and constant angle of 180 degrees. The peeling force-to-sustain data are thus the principal parameters characterizing the adhesive strength.
In general, a 180-degree peel test system consists of a universal testing machine, grips to hold the materials, and a speed controller to accurately control the speed of peeling. The test is performed by fixing the rigid substrate and then pulling the flexible material away from it in the opposite direction until the bond fails. Different environmental or operational conditions can be simulated during the test, such as temperature or humidity, to challenge specific use cases.
Given the nature of its application in manufacturing and industries such as packaging, automotive, and electronics, the adhesive performance ensures product reliability and safety. The data from the test allow manufacturers to validate adhesives, improve products, and gain feedback on industrial standards. The 180-degree peel test thus offers a point of standardized comparison by which adhesive systems can be evaluated.
Comparison of Different Types of Peel Tests
The primary types of peel tests include the 180-degree peel test, 90-degree peel test, T-peel test, climbing drum peel test, and floating roller peel test.
|
Test Type |
Angle |
Bond Type |
Material |
Purpose |
Key Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
180-degree Peel |
180° |
Rigid/Flexible |
Adhesives/Laminates |
Adhesion strength |
Peel force (N) |
|
90-degree Peel |
90° |
Rigid/Flexible |
Films/Coatings |
Adhesion toughness |
Load (N/cm) |
|
T-Peel |
Linear |
Flexible/Flexible |
Polymers/Metals |
Bond uniformity |
Force (N/cm) |
|
Climbing Drum Peel |
Rolling |
Flexible |
Composite Panels |
Peel energy |
Resistance (N·m) |
|
Floating Roller Peel |
90°+Roll |
Flexible |
Thin Laminates |
Dynamic peeling |
Adhesion rate |
Peel Test Applications Across Industries
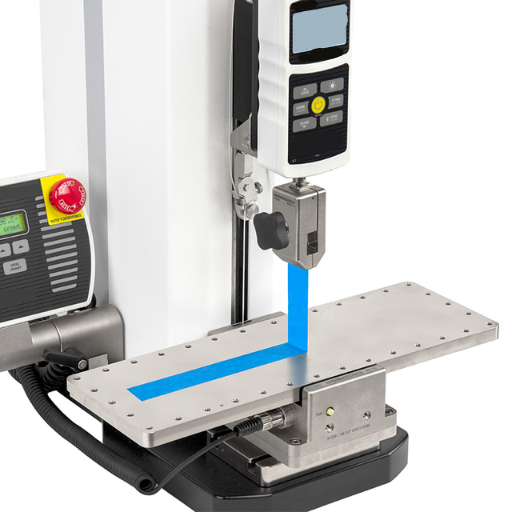

Peel tests find application almost anywhere adhesion performance needs to be evaluated.
1.Automotive Industry: To guarantee durability and safety of bonded components such as interior trims, panels, and weather seals, peel testing is carried out. The tests check for adhesion strength to survive operational stress such as temperature variations and mechanical vibrations.
2.Aerospace Industry: Peel tests analyze adhesion performance of composite panels and structural laminates to ensure lightweight yet strong assemblies. The climbing drum peel test is carried out to evaluate energy resistance under dynamic conditions.
3.Packaging Industry: Peel tests are carried out on flexible laminates and polymer films from the standpoint of seal application. The T-peel and floating roller peel tests are commonly applied to check bond uniformity and dynamic adhesion rates of packaging materials.
4.Electronics Industry: Used to verify the strength of bonded layers in devices such as screens, flexible circuits, and lamination films so that products hold up under thermal and mechanical stresses.
5.Construction and Building Materials: Adhesion tests help in developing coatings, adhesives and composites that can stand against environmental challenges through construction materials. Adhesion tests such as 90-degree peel are considered for application in evaluating bonding under various loading situations.
More importantly in specialized applications, these tests provide a link among adhesion strength, durability, and energy resistance toward ensuring material reliability and performance.
Packaging Industry and Adhesive Performance
Adhesive performance in the packaging industry dictates the integrity and longevity of packaged products. Tensile strength tests, shear tests, and peel resistance tests are carried out to assess the bonding strength under various stress conditions. Evaluation tests shall be performed with a view to determining whether the glue can withstand humidity, temperature changes, and mechanical pressure during transportation and storage. Advanced adhesives are formulated to meet the requirements of flexible packaging, corrugated cartons, and sealed containers, thus assuring greater product safety, less wastage, and more sustainability in global supply chains.
Automotive Applications of Peel Testing
In vehicles, peel testing is crucial to determine the permanence of adhesive bonds among various components. Especially among materials like metals, composites, and plastics frequently used in vehicle assembly, adhesion tested by peel methods holds importance. There’s a need to test bonded joints manifesting from bodywork to establishing trim and interior applications to check if they’ve got enough structural strength. Peel testing simulates the stresses that adhesive bonds might undergo during vehicle operation, such as vibration, thermal cycling, and mechanical loads, determining the durability and reliability of the adhesives. This, in turn, ensures that they comply with safety and quality standards while enhancing the longevity and performance of products in the harsh environment of an automobile.
Aerospace and the Need for Strong Adhesion
The conditions faced in aerospace where adhesives are required are considered extreme due to mechanical load, temperature gradients, and even chemical corrosive effects. The aerospace adhesion must be subjected to the best safety and quality standards since it is of a highly critical nature. All strong forms of adhesion are needed for composite structures, interior panels, honeycomb cores, and fuel tanks. The adhesives for use in aerospace are designed in some manner so as not to add much weight while giving enough structural strength to keep the fuel efficiency and performance intact. These adhesives are then subjected to testing programs involving shear, peel, and impact tests to prove their ability to sustain operational stresses typical of aerospace environments.
Peel Strength Testing Equipment
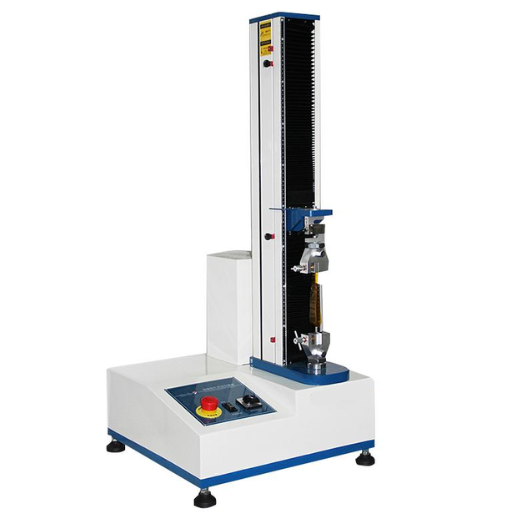

Peel strength testing equipment are designed to measure the adhesive bond strength between materials-the force required to peel apart the bonded assembly under controlled conditions. Usually, a universal testing machine working with an attached peel fixture, i.e., 180° or 90° or T-peel grip, is used according to the application requirement of the job. These machines provide the peel force value with great precision, allowing the adjustment of testing parameters in peel rate and peel angle to represent actual working conditions.
Overview of Testing Machines Used
According to my experience, universal testing machines with customizable fixtures constitute the common peel testing machines. These include 180°-degree, 90°-degree, and T-peel grips selected depending on the materials being tested and the application standards. I prefer these machines because of their accuracy in determining the peel forces and adjusting parameters such as peel rate, peel angle, and tension, in order to reproduce field conditions exactly. More developed systems have software interfacing for data analysis, resulting in thorough reports and recognition to reference testing standards such as ASTM and ISO.
Universal Testing Systems for Peel Strength
Universal testing systems for peel strength measurement are among the most versatile and commonly used for the evaluation of adhesive bonds, films, and similar materials. These systems basically apply tensile force in a controlled manner in order to measure the resistance offered by the material under certain test conditions as prescribed in a particular specification. Important features include different test rates applicable, application of loads at an angle, either 90° or 180°, and permitted load varied depending on the application in question and the types of materials involved and their thicknesses.
Universal testing machines of modern design boast digital interfaces and analysis software that allow for precise measurement and visualization of data acquisition in real-time. They ensure conformity to ASTM D903 and ISO 8510 standards under which peel testing procedures are carried out. Also incorporated in these systems are load cells and extensometers for accurate measurement of force and displacement, thus making a crucial appeal for industries requiring the reliable quality control and performance evaluation of adhesive products.
In addition to that, the universal testing systems show compatibility with a variety of test fixtures or grips, thereby constituting a very precious tool that will enable one to conduct a broad spectrum of peel, tensile, and shear tests on different substrate materials in the exact manner required.In this regard, through the incorporation of environmental chambers, some systems can simulate temperature and humidity, hence enabling testing that mirrors real-life applications. With such versatility and accuracy, universal testing systems serve as tools for a myriad of research, development, and quality assurance undertakings.
Calibration and Maintenance of Testing Equipment
Calibration and maintenance are essential for checking the accuracy and reliability of the testing equipment. I monitor the maintenance schedule as well as the procedure for calibration in adherence to an industry’s specification and manufacturer’s instruction. This involves the calibration of the equipment to adjust to a known reference value that is accepted as a set value; in doing so, conformity to the specified standard is tested. Maintenance-wise, I check on a regular basis for any excessive wear or damage to any load cell or sensor, clean every element in motion, and lubricate any moving part that could impede operation if left unattended. All calibration and maintenance records are kept to maintain traceability and maintain the integrity of testing.
Best Practices for Accurate Peel Testing
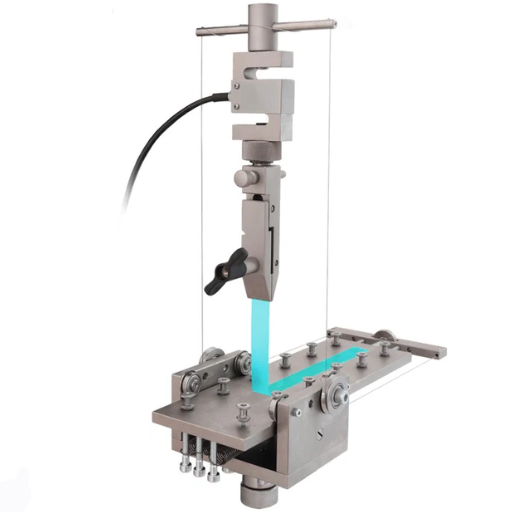

To obtain accurate peel test data, it is imperative to implement strictly standardized procedures and consistent test conditions. Selection of appropriate test equipment and verification of its calibration before use must precede specimen preparation. Test specimens must be prepared very carefully so their size, surface condition, and adhesive application are all uniform. Tests should be carried out in a controlled environment where major variables, such as temperature and humidity, are monitored and maintained because these factors might affect the results. The test equipment is also to be operated at a constant peel speed as set forth in the applicable standard. Test information and results must be documented in a systematic manner allowing for complete repeatability and traceability of test results.
Sample Preparation Techniques
Sample preparation goes a long way toward ensuring reliable and reproducible results in testing. Select materials that meet the predefined specifications so that the test results are consistent for such properties as thickness, composition, and surface features. Clean the surfaces to eliminate contaminants such as oil, dirt, and oxidation that might hinder adhesion or alter the measurement’s accuracy. Apply adhesives in a consistent manner in accordance with the manufacturer’s directions. Avoid air bubbles or any inconsistencies that might affect test results. Cure the prepared samples under prescribed conditions to promote bonding and stabilization, allowing test samples to maintain accuracy and integrity during testing.
Environmental Considerations in Testing
I chiefly look to control variables such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants when looking at environmental considerations in testing. An environmental factor can significantly affect the results of a test; thus, I ensure a uniform conditioning process for all equipment and samples immediately before testing. For example, constant temperature and humidity conditions guarantee that there is no degradation of materials under study and therefore that test results are repeatable. Contamination can be minimized by using a clean, controlled environment and proper sample storage methods. Following these approaches, I ensure both test accuracy and reliability while taking external environmental factors into consideration.
Ensuring Proper Calibration for Reliable Results
Calibration being able to be considered one of the most important tools to guarantee reliable, consistent results is synonymous with its being a process whereby measurement instruments or a system will be compared against known standards so as to note deviations and therefore rectify them. This can be achieved by using traceable standards that in most cases are certified by agencies such as the NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology). Calibration intervals should always be respected once set so conduction of these adjustments can be guaranteed.
Another issue to give special attention to is the calibration environment, which might be a major source of errors due to temperature, humidity, vibration, etc. All calibration procedures should be well documented, and records should be kept since these are required for traceability and accreditation to be considered under accepted industry standards such as ISO 17025. The documents serve not only to declare an instrument’s state of accuracy but also to participate in assisting, at least partly, in determining the root cause of a discrepancy. This way, the operator is assured of a great precision or reproducibility in his measurements.
Reference Sources
- Peel Strength Testing – The Complete Guide – A comprehensive guide on peel strength testing and its applications.
- Peel Strength Testing – Explains the calculation and significance of peel strength in adhesive testing.
- Peel Testing | An Introduction – Provides an introduction to peel testing and its importance in evaluating adhesive bonds.
- Peel Test – Discusses the methodology and importance of peel testing for adhesion strength evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q:A peel test and why is it important?
A:It is a peel test to determine the peel strength of the glue bonds between two surfaces. The shear force is measured to detach the adhesive from the substrate at some given angle, usually 90° or 180°. Understanding peel strength is necessary to make sure that the adhesives are put to good use in different industries such as automotive and construction.
Q:What are the different types of peel tests?
A:There are several kinds of testing, including 90° and 180° peel. The 90° peel test checks the force needed to peel an adhesive at a right angle, while the 180° peel test measures the force applied when the adhesive is pulled away from the substrate in a straight line. Hence, it basically tests the strength of the adhesive bond under various conditions.
Q:How does one measure the peel strength of an adhesive?
A:The peel strength is determined by conducting peel tests where the adhesive bond is subjected to a controlled force until separation occurs. The average force per unit width is calculated throughout the test in order to measure the adhesive strength under defined conditions.
Q:How important does the peel angle become in peel tests?
A:The peel angle, such as 90° or 180°, will greatly affect the peel test results. Different levels of stress are transformed through the adhesive bond according to variations in the peel angle, which affect peel strength measurements. The efficacy of testing and comparison between different adhesives depends on carefully selecting the peel angle.
Q:What is the average force measured during a peel test?
A:The average force measured during a peel test, also known as peel strength, is the applied load that is summed to separate an adhesive from the substrate over a predetermined width. This metric is fundamental in the evaluation of adhesives for field applications.
Q:What industrial capabilities do the peel tests find?
A:Within material testing, peel test applications include evaluation of adhesives for automotive-type adhesives, packaging materials, and construction materials. Other issues addressed by the test concern the durability and reliability of adhesive bonds under different conditions.
Q:What is the equipment used to conduct peel tests?
A:Peel tests can be conducted by means of a testing machine/test frame particularly designed for peel strength testing. These machines measure forces exerted during the test and can be adjusted to vary the test speed to simulate conditions the adhesive would meet in an actual application.
Q:How is a wet-peel test different from a standard peel test?
A:In a wet peel test, for example using the floating-roller method, one tests the adhesive’s performance when exposed to moisture. Such a test is essential for investigating the peel resistance of high strength adhesives in circumstances where water-finding consideration comes into play, thus allowing for an assessment of how durable an adhesive bond remains under wet conditions.






