Corrugated board, with its strength, durability, and multifaceted uses, is a key material in the packaging industry. Flat crush resistance is among the critical properties that determine its performance, being the property of resisting compressive forces from above. Knowledge of this property is crucial for manufacturers, quality control personnel, and supply chain managers seeking to deliver products that are reliable and well-protected during storage and transit. This article focuses on the Flat Crush Test: Ways and Means, Implications for Corrugated Board Performance. You can optimize packaging design or work toward satisfying industry specifications with technical insights on evaluating and improving the flat crush resistance of your materials presented herein.
Introduction to the Flat Crush Test
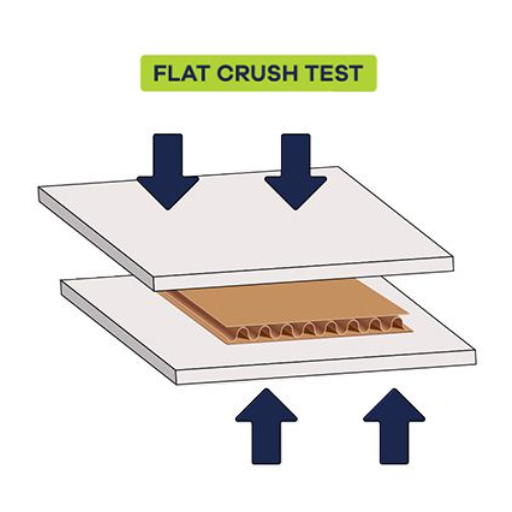
The Flat Crush Test provides an industry-standard method for testing the strength and durability of corrugated board. It measures the resistance of the vertical crushing forces applied perpendicular to the board’s surface. This test defines material behavior under compressive stresses during stacking, shipping, or handling. With flat crush resistance data at hand, manufacturers can thus ascertain that the corrugated board complies with selected standards required for packaging and shipping.
Definition of Flat Crush Test
The Flat Crush Test is a standardized method of measurement that assesses the strength and durability of corrugated board by evaluating its resistance to crushing forces applied perpendicular to the surface. Recent industry data and developments from international packaging standards organizations indicate that flat crush resistance remains a crucial parameter for evaluating a corrugated board’s ability to endure compressive stresses during storage, stacking, and transportation. New developments emphasize that measurement systems, including automated ones, offer more accuracy and reproducibility, hence improving new testing protocols. Such improvements enable manufacturers to meet more stringent packaging standards while maximizing material-use cost efficiency and promoting environmental sustainability. Packaging stakeholders can leverage such data to ensure that corrugated products meet uniform quality and functional standards in various applications across diverse supply chains.
Historical Context of Flat Crush Testing
Flat crush testing has undergone significant evolution over the decades to keep pace with the ever-growing requirements of industries engaged in packaging. Initially, testing was experimental, involving the manual measurement of the force strength of corrugated materials. The earlier methods lacked the necessary repeatability and precision to ensure consistent quality control. Over time, testing equipment has evolved in sophistication, incorporating accuracy through automation and digital techniques that assess material strength and accommodate the needs of high-volume production and stringent industry standards. The establishment of standardized testing procedures further ensures that results from different third-party manufacturers differ by an area and provide unselective testing evaluations from flat crush testing, a prior candidate in assessing corrugated testing.
Importance of Flat Crush Resistance
Being tested for the material’s ability to withstand compressive forces, flat crush resistance is one of the critical performance characteristics of corrugated materials. This characteristic is important because it provides strength to the packaging when it is placed under loads during storage and transportation. The more flat crush resistance they have, the better they ensure protection of the contents of the package from damage and in the use of the environment where stacking pressure or incidence of some physical force would come. Additionally, it proves to be the least helpful in material utilization formation during the packaging process, in terms of trade-offs between strength and cost.
Purpose of the Flat Crush Test
Flat crush testing is performed to evaluate the compressive strength of corrugated boards or similar materials subjected to a perpendicular force. This test measures the material’s resistance to crushing and determines its suitability for packaging applications that require durability and structural support under load.
Assessing Material Strength and Durability
Material strength and durability are the two crucial elements required to determine the real-life performance of the corrugated board. Strength is the measure that is inferred mainly using edge crush tests (ECT) and flat crush tests, which correspondingly analyze the ability of the board to resist compressive forces perpendicular to it or along its edges. Durability refers to the resistance of a material to adverse impacts, such as wear, fatigue, and environmental factors, over time.
Dependent factors concerning these tests will be the quality of linerboard and medium, glue factors, and flute size. For example, a higher ECT value would indicate that the better the load capacity for stacking, i.e., during transportation or storage. The FCT would give an indication of how stable this board is when pressure is applied to its surface. Based on the test results, manufacturers will select arrangements of corrugated materials that offer a better trade-off between cost and performance, tailored to the specific packaging needs of the customer. Understanding the interactions between material elements and external forces is crucial in developing the most capable and cost-efficient alternative for a particular set of operational requirements.
Quality Control for Manufacturers
A Flat Crush Test (FCT) measures compressive strength of corrugated board components by testing for the ability to resist crushing forces applied perpendicularly. This test ensures that the materials used for packaging, storage, and transportation will withstand and perform as expected. Identification of weak points in the corrugated material will optimize the design for reliability while considering cost in the production process. Ultimately, FCT maintains consistently high-quality packaging solutions in all industrial environments.
Impact on Packaging and Shipping
From my perspective, the flat crush test is essential to ensure packaging materials remain structurally intact during handling, storage, and shipment, thereby minimizing the risk of damage to the contents and ensuring utmost customer satisfaction. Additionally, conducting flat crush testing enables me to select materials that meet durability requirements while enhancing cost efficiency in production. It also helps me identify design flaws that can be addressed to provide better protection to products under various shipping conditions.
Conducting the Flat Crush Test
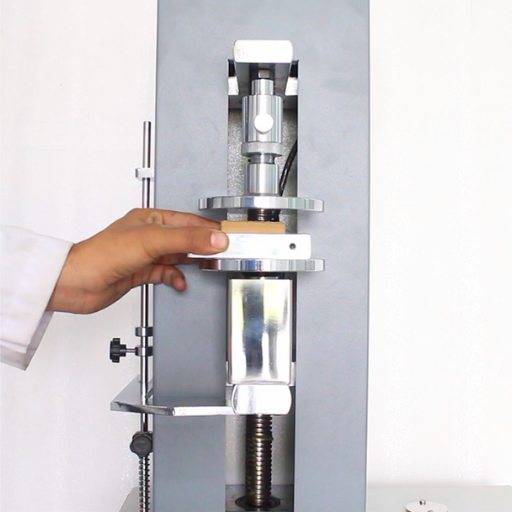

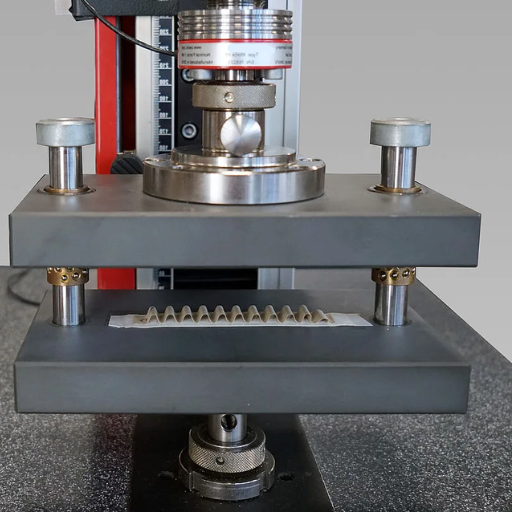
A sample piece shall be made by cutting a piece of corrugated board of the given dimensions, laid down according to the standard testing procedure, e.g., TAPPI or ISO. The sample is then placed between the platens of a compression tester, which applies a compressive force steadily increasing until the sample fails. The maximum force sustained by the material up to failure is noted. This force measurement directly evaluates the resistance of the corrugated board to crushing forces, which in turn is used for studying the board’s packaging considerations under different loading conditions.
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Preparing the Test Specimen
Ensure the corrugated board specimen is cut to the specified dimensions, without any imperfections such as tears or creases. Employ a cutting guide or template for precise and consistent sample sizing. - Calibration of Equipment
Verify that the compression tester has been calibrated satisfactorily according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Look for any signs of wear or malfunction that may affect the accuracy of the results. - Adjust Test Settings
Set the compression tester to follow the respective testing method specified in TAPPI or ISO standards for the test. Set the compression speed and other parameters accordingly as required by the procedure. - Insert the Sample
Place the specimen correctly in the compression tester between the platens, ensuring it is properly aligned to avoid uneven load application during the test. - Test Conductance
Begin by applying a steadily increasing compressive force to the sample. Continue to monitor the equipment for uniform application and note any irregularities observed during the testing process. - Record the Data
Record the maximum load sustained by the sample before structural failure took place. Ensure that the figure is recorded in a timely manner, either automatically by the tester or manually by the operator. - Analyze the Results
Interpret the measured loads in relation to established performance limits or customer requirements to assess the sample’s acceptability for the practical applications being considered. - Test Documentation
Compile all observations, measurements, and results into a detailed report. Include information on equipment settings, ambient conditions, and any deviations from the standard procedure, if relevant.
Ensuring Accuracy in Testing
Testing accuracy must be ensured through rigorous adherence to procedural standards and strict application of precise measurement equipment. To maintain reliability and consistency, equipment must undergo regular calibration. Moreover, without controlled environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, the impact of outside factors might prejudice the results. Then there should be harshly monitored validation procedures for verifying the repeatability and reproducibility of testing results. Furthermore, training of personnel is essential to reduce human error, so that all testing operators adhere to best practices and standard methods.
Common Standards and Protocols (TAPPI T825)
TAPPI T825 is used as a standard method to characterize the edgewise compression strength of corrugated board, making it a faithful indicator of packaging material performance. The standard lays down very precise parameters, which include the preparation of specimens, calibration of equipment, and the performance of tests, to ensure that the results obtained are uniform and repeatable. Specimens shall be prepared to uniform dimensions in such a way that the cut edges do not affect the test results. It is essential to calibrate the compression testing equipment to eliminate possible errors caused by misalignment or inaccuracies in the equipment itself.
This protocol, therefore, places great emphasis on maintaining controlled conditions in the testing environment, including standardized, measured temperature and relative humidity at 23°C and 50%, respectively, in accordance with stated industrial norms for material testing. Environmental consistency is thereby maintained. The corrugated materials used are subjected to compressive forces measured perpendicular to the edge until failure, and maximum resistance forces are recorded. The TAPPI T825 framework can be used to determine the strength, durability, and overall suitability of corrugated board for industrial applications, providing a quick reference to highly demanding standards for packaging performance predictions.
This evaluation methodology is fundamental to manufacturers and researchers involved in scientifically realizing design enhancements and reductions in waste, as well as protection optimization during distribution, utilizing reliable and universally accepted measurement protocols.
Equipment Used in Flat Crush Testing
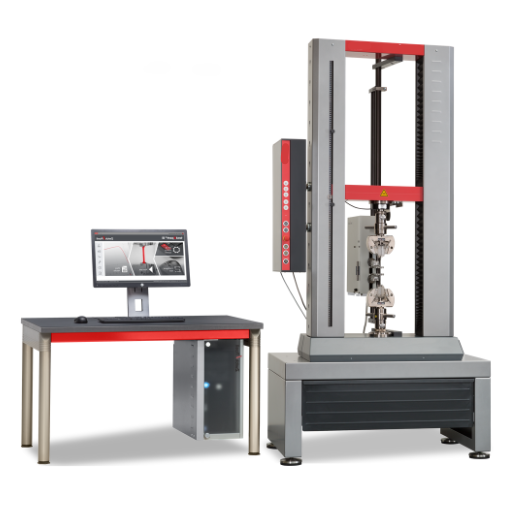

For flat crush testing, the equipment must be highly standardized to accurately assess the strength and performance of the corrugated board subjected to compressive forces. Some key components are:
| Equipment Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Compression Tester | Calibrated equipment designed to apply a uniform compressive force | Usually includes load cells for weighing resistance |
| Test Platens | Smooth rigid surfaces | Apply pressure uniformly with minimal variable interference to results |
| Sample Cutter | Precision cutting tool | Preparing test specimens with accurate dimensions for conformity to standardized testing requirements |
| Environmental Chamber | Climate-controlled facility | Maintenance of ambient temperature and humidity in testing to replicate the usage environment |
Such equipment would ensure that the results were consistent, repeatable, and conducted in accordance with the established industry standards.
Overview of Crush Testers
Crushers are a set of instruments designed to test for compressive strength or resistance of the wanton materials, which may include paper and cardboard, among others. Therefore, these apparatus find application in packaging, materials science, and manufacturing where it becomes crucial to know one’s strength being tested to give a certain degree of durability-effect-based. These devices frequently measure parameters like the edge crush test (ECT), flat crush test (FCT), or ring crush test (RCT), depending on the application and material characteristics.
Latest keyword data from Google search trends indicates that inquiries regarding crush testers primarily concern their accuracy, calibration, and whether they meet international standards such as ISO or ASTM. These questions underscore an unmistakable emphasis on city tourist attractions, ensuring the reliability of product performance and conformance to industrial standards. Modern-day crush testers answer these queries with a plethora of features, including digital interfaces that allow for real-time data acquisition, automatic calibration procedures, and the ability to perform multiple tests, thereby ensuring thorough inspection with minimal user effort. In this combination of accuracy, speed, and certification lies their utilization for traceability in quality assurance processes for material testing.
Key Features of Flat Crush Testers
Digital Precision and Real-time Data Acquisition
Modern flat crush testers are equipped with a digital interface for real-time measurement of data, enhancing the reliability of test results.
Automated Calibration Systems
These machines are designed with automated calibration protocols to maintain a consistent performance relative to industry standards.
Multi-test Capability
Advanced models will support various types of crush tests, such as edge crush, ring crush, and flat crush tests, thereby allowing for considerable versatility in material testing.
Ease of Use
User-friendly controls and transparent instruction screens help simplify the testing process, removing the complexities of operator error.
Robust Build Quality
Constructed with durable materials, these testers are designed to withstand repetitive use while maintaining precision over an extended operational lifespan.
Advancements in Testing Technology
Recent advances in flat crush test technology have focused on improving accuracy, efficiency, and data integration. This implies that modern flat-crush testers have been equipped with higher-resolution sensors, capable of measuring with greater precision; hence, much better repeatability of testing results can be ensured. Automation also plays a significant role in these developments, with the motorization of platen movements in many systems and digital interfaces enabling widely connected operation. Enhancements to data connectivity further propagate integration with laboratory information management systems (LIMS), thus enhancing the availability of data storage, fundamental analysis, and subsequent report generation. These advancements reduce the likelihood of human error, enhance test throughput, and ensure compliance with stringent confidentiality standards.
Industry Applications of the Flat Crush Test

The Flat Crush Test has widespread applications across industries that work with corrugated materials, including packaging, logistics, and manufacturing. With raw materials and packages being handled by the packaging industry sector, it assesses the strength of corrugated sheets to ensure that they can sufficiently protect the packages during transit and storage. Logistics incorporates this test to determine how materials will behave under compression, which is crucial for stacking and handling processes. Manufacturers include this test in their quality control checks to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and customer specifications for strength and consistent performance. Knowledge about crush resistance, gained through testing, is most helpful in optimizing products for compliance by all the above industries.
Role in Packaging Safety
The flat crush test plays a crucial role in packaging safety by measuring the resistance of corrugated materials to external compression forces. Such an ability is fundamental in preserving the integrity of boxes about stacking, storage, and transportation, thereby minimizing the risk of damage to the products. The flat crush test ensures reliability of a packaging wherein, in the conduction of flat crush testing, the packaging should not collapse and adversely affect load stability; flat crush test objectives thus align with industry standards on safe-performing materials.
Significance in Product Protection
The Flat Crush Test (FCT) provides an essential check on the rigidity and strength of corrugated materials, primarily from a top-to-bottom compressive point of view. From my research, this test measures the resistance to crushing of the fluted layer, allowing the materials to withstand the pressure caused by stacking and transit without compromising the integrity of the structure. This is crucial in protecting a product from deformation or damage during harsh environmental exposure. The FCT also ensures quality control by certifying the performance standards of corrugated boards, thereby ensuring dependable product protection while maximizing material utilization.
Examples of Use in Various Industries
- Food & Beverage Packaging: Tests safety by ensuring that the corrugated boxes for transporting glass bottles or perishable goods can sustain stacking pressures and do not collapse under load, thereby compromising the product during distribution.
- E-Commerce/Retail Logistics: Testing for the durability of packaging materials against stresses during handling and shipping to safeguard items from damage.
- Pharmaceutical Packaging: Ensuring that corrugated packaging maintains its structural integrity in controlled environments (e.g., cold storage) to protect sensitive medical products and equipment.
- Electronics Transport: Ensure the packaging’s ability to resist external forces, providing adequate protection for high-value items such as laptops, desktops, and smartphones during transit.
- Industrial Goods Shipping: For the large, heavy-duty corrugated containers used for machinery and equipment, it verifies the strength against structural failure during shipping in the most demanding conditions.
Reference Sources
-
Flat Crush Test (FCT) on Corrugated Board | ISO 3035 – This source provides insights into the flat crush test as per ISO standards.
-
Flat Crush Test of Corrugated Board (Flexible Beam Method) – A detailed document on the flat crush test method by TAPPI.
-
Flat Crush of Corrugated Board Test – Explains the flat crush test procedure and its significance in evaluating corrugated board strength.
-
TAPPI T825 Testing – Information on the TAPPI T825 standard for flat crush testing.
-
Calculation of Corrugated Board Flat Crush Resistance – A research paper discussing the parameters and calculations involved in flat crush resistance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is the Flat Crush Test and Why Is It Important in Corrugated Board Testing?
The flat crush test is a standardized method for determining the flat crush resistance of corrugated materials, primarily corrugated paper. The test is conducted to enable a manufacturer to examine the strength properties of its packaging system and ensure that it will withstand the rigors of transportation and handling. Flat crush resistance enables companies to enhance their packaging design for improved performance.
How Does the TAPPI T825 Flat Crush Test Work?
The TAPPI T825 flat crush test uses a testing machine that applies lateral pressure to a sample of corrugated board. The force required to crush the horizontal surface of the board is measured during the test, providing helpful information about its resistance behavior and overall strength. This method, being widely used in the industry, remains accepted in rendering sincere test results.
What Types of Corrugated Boards Are Tested for Flat Crush Resistance?
Different types of corrugated boards are tested for flat crush resistance, including single-flute, double-faced, double-wall, and triple-wall corrugated boards. They all have varying structural properties, and each is designed for a specific application, thus necessitating the evaluation of their flat crush resistance.
What Is the Equipment Used for Conducting a Flat Crush Test?
Tests for flat crush resistance involve specialized equipment such as a testing machine capable of applying controlled pressure on corrugated samples. This constitutes the utmost requirement for calibrated machinery that accurately measures the compressive strength and resistance of the test specimen, specifically the corrugated material.
What is the Importance of Measuring Flat Crush Resistance for Packaging?
This resistance is measured to be sure that the packaging can withstand a certain amount of external forces during shipping and handling. Flat crush strength helps manufacturers ensure that their products do not suffer damage, thereby preventing waste and ensuring a positive customer experience. High flat crush resistance packages ensure more protection for the given objects.
What Units of Measurement Are Used in Flat Crush Testing?
The results of flat crush testing are most often reported in kilopascals (kPa), which describe the amount of pressure applied to the corrugated material during the test. This unit of measurement helps standardize test results and facilitate comparisons between varying materials and designs.






