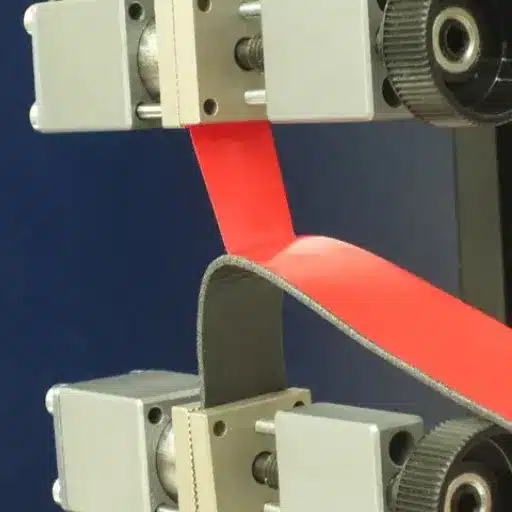
Adhesive-peel-strength tests are by far the greatest tools in ensuring the reliability of putative bonding and in desired performance. In an array of industries-far-and-away, from aircraft installations to surgical instruments to consumables-purposeful adhesives serve the role of bonding materials. But how does one measure the strength and durability of the bond? Understanding what peel strength means and the methods used in testing it is crucial to manufacturers intending to improve product quality and perpetuate the demand for standardized industries. In this article, we shall look into the bare basics of adhesive-peel-strength knowledge, discuss why testing is essential, and finally go through novel testing solutions to optimize applications and lend an assured finish. Whether you are an engineer, a QA analyst, or even just particularly curious about that elusive bonding concept, we hope that this will give a few good insights into the world of adhesive-peel-strength testing.
Introduction to Peel Strength

Definition of Peel Strength
Peel strength refers to the force required to peel two bonded materials. The force is typically exerted as a flexible layer being pulled away from a rigid or comparatively less flexible substrate. This measurement helps determine adhesive performance under other conditions and the durability of materials in various industries ranging from packaging to construction, and a bit of automotive.
Peel strength values are always brought in respect to force per unit width (N/m, pounds/inch). This is an important fact that enables engineers to guess if adhesives will stand mechanical stresses, environmental factors, or prolonged use. As a matter of fact, peel strength is used to make sure adhesives perform adequately at working conditions, or under stressors such as heat, moisture, or vibration.
The peel strength test is a fundamental bonding evaluation to ascertain whether a solution meets a particular set of application requirements. By accurately determining the force necessary to peel bonded materials from one another, manufacturers and engineers decide on an appropriate adhesive, the way to apply it, and product design that is justified under closures of performance requirements for various applications.
Importance of Peel Strength in Adhesives
Assessing peel strength forms the first step in determining whether an adhesive solution can really be considered effective and reliable in varied applications. The peel force determines essentially the force necessary to separate two bonded surfaces while the surfaces are pulled apart at a particular angle-signifying the performance of an adhesive under real conditions. This property of adhesives is important especially in applications of the automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics industries, wherein adhesives sustaining mechanical stresses and environmental factors for the sake of long-term integrity are mandatory.
In view of the above definitions, peel strength of an adhesive is that meaning it shall resist the force of shear or tension without exhibiting failure of the bond. These peel strength considerations become important in the consideration of the products, or structures, moving or shaking or being stressed alternatively for unforeseen detachment or structural compromise. This facilitates the engineering and manufacturing of adhesives suitable to the load and environmental conditions they expect, thereby making sure the products satisfy safety and functional standards.
Further, peel strength can also be the parameter to test for material compatibility; not all adhesives adhere well to all surfaces; it must be tested to see whether it will adhere well without harming the materials involved. By extending the analysis of peel strength as an ostensibly major parameter in the development process, manufacturers can therefore guarantee product durability, hence minimizing the chances of failure and hence customer satisfaction in varied and harsh environments.
Applications of Peel Strength Testing
The peel strength test has become a key step in various industries to ascertain the performance, durability, reliability, and bonding of the materials. Some of the key applications are:
Automotive Industry
In adhesives, the automotive sector finds applications for body panel assembly, interior component assembly, and electronics assembly. Peel strength analysis works to ensure that the adhesive bonds withstand dynamic stresses in automotive environments, harsh weather conditions, and prolonged UV radiation. Studies from the industry report that improvements in adhesives have helped reduce automotive weight by 10%, thus aiding in better fuel efficiency, while on the other hand, maintaining the safety and durability of the vehicle.
Aerospace and Defense
These things require adhesive bonding to keep together under extreme temperature and pressure variations or while subjected to mechanical stresses. In this particular area, peel strength testing is obligatory to ascertain the safety of components such as panel assemblies, structural reinforcement, and thermal insulation. Apparently, with newer adhesives made for aerospace applications, bond integrity has improved by almost 20% as per recent advancements in bonding technology.
Electronics and Semiconductors
The electronics industry uses peel strength testing to measure bond strength of films, solder masks, and flexible circuits. This hence became essential to check for device life in the case of mobile phones, laptops, and wearables. Thin-film adhesion has demonstrated that a stronger adhesive bond might enhance product life by as much as 15%.
Packaging Industry
In food packaging, medical supplies, and consumer goods, adhesive seals must meet the highest barrier requirements to prohibit contamination or leakage. Peel strength testing is extensively carried out to check the strength of a seal and its durability. According to recent data, packaging reliability witnessed a 30 percent improvement with the advent of polymer adhesives.
Construction and Infrastructure
With adhesives for floorings, panels, tiles, and façade works, peel strength is one of the most sought-after parameters. A rigorous peel test allows the verification that the surfaces remain secure even when loaded and under environmental conditions. Studies stress that high-performance adhesives, having high peel strength, have brought great savings in maintenance costs.
Medical Equipment
The adhesives must reliably work and must also be free from any hazards on patient safety. Peel strength testing leads to ensuring that, while exposed to water or body heat, the adhesive can still bond. An example of improvement in a medical-grade adhesive is the development of a new adhesive with an improved wear time for prosthetics, providing a 25% increase in adhesive performance.
Such examples underscore the essence of peel strength testing in the assurance of safety and customer satisfaction in quality, product development, and industry across various application areas.
Peel Strength Measurement Techniques
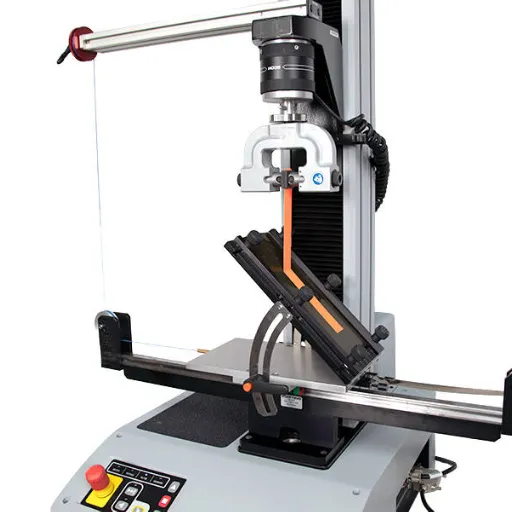

Using a Universal Testing Machine
The UTMs are ubiquitous testing machines that can be set up to measure the peel strength of adhesives by exerting a mechanical test with controlled parameters. A well-defined tensile force along with a speed of application, is fixed onto the adhesive bond to simulate conditions similar to real life, with records kept of the force required to fail the adhesive bond, thus indicating as to how strong and how well the adhesive may have performed. The whole process is an accurate and reproducible method of testing peel strength and is thus commonly chosen in industry.
An adhesive sample must be prepared for the peel strength test in a manner that corresponds to the presently followed testing protocols. One end of the materials with an adhesive bond between them under test gets clamped in the grips of a UTM, while the other end is pulled down and peeled away under tension. Force measurements during the peeling process are continuously monitored and recorded by the UTM. This force, often depicted as a graph, is used to verify intervening factors that work for or against the adhesive bond under particular conditions.
Advantages afforded by this instrument include forceful control with precision, proper data collection, and variations of test protocols applicable to many different adhesive types and applications. With standardized results at descriptive the UTM assists in research, development, and quality control processes to ensure that adhesives can fulfill promises being made for the medical, industrial, and consumer product applications.
Understanding Pressure-Sensitive Peel Tests
Pressure-sensitive peel tests are necessary for the evaluation of the adhesive strength of pressure-sensitive materials. The peel tests ascertain the amount of force needed to remove an adhesive material from a surface, thus deriving valuable information on its performance and reliability. By definition, the test involves placing the specimen on a standardized surface, after which a controlled force is exerted at a constant speed and angle to peel it from the surface.
The results of pressure-sensitive peel tests are indicators of how long the adhesive will last, how flexible it is, and whether it is suited to a given application. These tests assume critical importance in industries utilizing adhesive materials under varying application conditions, with medical applications on one end, packaging in the middle, and electronics on the other. Based on peel strength, manufacturers and researchers can come to grips with how well an adhesive would perform and how well it would adhere under various working conditions.
Standardized peel tests also contribute to quality control and product development of the adhesive. The standardized peel tests offer manufacturers a chance to compare different adhesive formulations and determine which areas require improvement. When reliable and reproducible results are obtained, they help in the streamlining of production processes and in ensuring that the adhesive always performs in the meantime, building up its reputation while being marketed to final consumers and other end users.
Adhesive Strength Measurement Protocols
Standardized tests provide proper methods to measure the adhesive strength and, more importantly, to be sure of the measures under given conditions. Two major types of adhesive strength tests used widely are the peel test and the shear test. These tests give valuable information about an adhesive’s resistance to forces applied in different directions and ensure the practical application of an adhesive.
The peel test measures from a given the force used to pull apart two bonded materials. The angles of 90° and 180° are generally considered standard angles. Such a force measurement is principally applied to adhesives associated with a film, tape, or other flexible materials. Meanwhile, the shear test measures the ability of the adhesive to bond two surfaces held under a constant load parallel to the bond. This test is generally used for structural adhesives that are required to resist heavy shearing forces.
Protocols per ASTM or ISO basically standardize methodology. Appropriate preparation of test specimens and conditions, calibration for correct set-up, and correct procedure would lead to good results. Thus, in assessing the performance of the adhesives, and also subsequently in product development and quality assurance, these proper measurement protocols are followed to ensure manufacturers have a better chance of making a sound decision.
Test Procedure for Peel Strength Testing
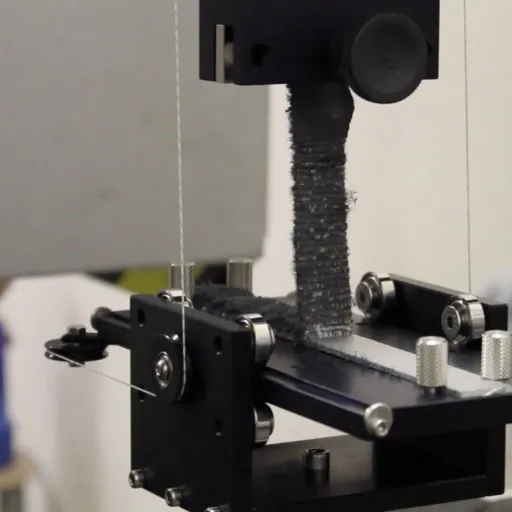

Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting Peel Strength Tests
- Preparation of Test Specimens:
Cut the specimens precisely to the measure or dimensions stated in the governing standard or test method. Apply the adhesive evenly on the bonding area, making sure there are no air bubbles or irregularities. Then cure under the conditions specified for that adhesive, such as time, temperature, or pressure.
- Set Up the Testing Equipment:
Calibrate the test machine strictly according to the manufacturer’s instructions and to test parameters required by the user. The specimens must be aligned in the grips with utmost perfection, as any misalignment can cause slippages or lateral forces affecting the output results. Adjust the peel angle to be reapplied, which is usually either 90° or 180°.
- Conduct the Test:
The machine should be started with the loading rate kept constant throughout the procedure, as specified in the chosen standard. Record the initial peel force. Monitor the entire peel force performance till the bond fully disengages. Observe any abnormality, such as sudden drops in force as these may indicate the existence of flaws in the adhesive bond.
- Analyze and Document Results:
After finishing the test, analyze the data to derive the average peel strength value, typically considered force per unit width (such as N/mm). Note any observations concerned with modes of failure, which could indicate whether there was cohesive or adhesive failure. Proper documentation guarantees that insights obtained through the test become both repeatable and reliable.
Common Challenges in Peel Strength Testing
Peel strength testing may encounter several challenges; these challenges contribute to the inaccuracy and unreliability of the results. The first of these is improper sample preparation. If the samples submitted for testing have not been prepared with accuracy, it can lead to a differential bonding situation that ultimately alters the result. Uniform application of the adhesive can eliminate this problem, while also ensuring the test materials are cut to the correct dimensions.
Another challenge is variability in the testing equipment or conditions. The influence of slight misalignments in the clamps, incorrect peel angle setting, or specified environmental factors (temperature and humidity) cannot be disregarded. Equipment should always be calibrated to reduce these effects and, to ensure repeatability, all parameters should then, be kept constant throughout the testing application.
Finally, the analysis of the results may become complicated if multiple failure modes come into play. It is necessary to carefully distinguish between cohesive failure, adhesive failure, or substrate damage through utmost observation and analysis. Detailed documentation and adherence to recognized testing standards assist in achieving the correct understanding and conversion of any failure mechanisms observed during the tests.
Interpreting Test Results and Data Analysis
The peel strength test quantifies the adhesive bond strength between any two materials by placing a known force on the separation at an angle and speed within predefined limits. Being used in such applications helps to check the durability and reliability of adhesives. More peel strength means a stronger adhesive bond that will stand greater forces during actual operations.
Interpretation of peel strength results must take into consideration of the material properties and the setup for testing, together with any environmental variables that could affect the outcome. For example, keeping the environmental conditions the same in terms of temperature and humidity is of utmost importance so that the results can be compared. Also, peeling speed and angle of peeling should agree with standard test protocols, yielding more insight.
Analyzing data means determining any trends or abnormalities within the test results. If a lesser peel strength is realized, factors such as inadequate surface preparation, cure time, or incorrect material combination must be considered. Accurate documentation of the testing process and test results gives a clear understanding of adhesive performance, thus assisting decisions on improvements or further testing, if necessary.
Peel Testing Standards and Regulations
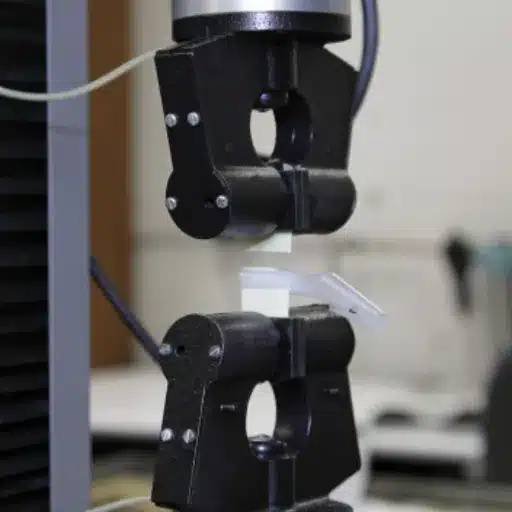
Overview of Industry Standards for Peel Testing
Peel testing standards do vary for industries but are chiefly aimed at ensuring uniformity in the assessment of adhesive strength and durability under given conditions. Some standards include ASTM D903 and ISO 8510-1, both providing guidelines for carrying on testing of the peel, according to parameters: preparation of the specimen, test procedure, and measurement accuracy that can be accepted. These standards ensure that any results can be reliable and repeatable between laboratories and in industrial settings.
ASTM D903, the dominant Standard, deals with adhesive peel or stripping strength and specifies methods according to materials, which include tapes and laminates. Requirements are laid down about the test equipment, specimen dimensions, and peel angle to maintain uniformity in testing methods. In contrast, standards issued under ISO 8510-1 provide general methods of determination of bond strength of adhesive joints, thus serving to compare the adhesive performances under standard conditions.
Such industrial standards guarantee the quality and safety of products, as well as compliance. By complying with such standards, manufacturers can test and compare adhesive performance, thus forming the basis for quality control, the development of products, and regulations for compliance. When the industry follows recognized standards, it ensures that testing results will continue to maintain uniformity, with an implicit guarantee that adhesives will continue to perform well in their own applications.
Compliance with Testing Regulations
Basically, there are testing regulations with which one has to comply to maintain quality, safety, and reliability levels for adhesive products. Testing regulations are there to ascertain that the performance characteristics and safety requirements are met by the product before it proceeds to the market. Manufacturers abide by such testing regulations to ensure that the adhesive in question actually performs under application instead of becoming a hazard or a failure in its real-world application.
Such regulations are generally fixed by national or international authorities to ensure uniformity across the industry. Testing parameters might include bond strength, durability, and resistance to climatic conditions. Great trust in product reliability and utility across modes of applications can be bestowed on producers and consumers if indeed the standard methods have been used in the testing of products. Compliance shall also abstain from legal penalties that could threaten a business and provide assurance to the environmental and safety statute levels for the product in question.
Eventually, testing fosters commercial improvements, counterbalancing the general innovations behind accountability. Manufacturers would be motivated to improve their products in conformity with standards, thus raising the bar for adhesive performance and sustainability. Testing and compliance protect end-users and, concurrently, raise industry standards, resulting in competition within a permitted environment.
Impact of Standards on Adhesive Performance
As a critical point, standards ensure consistent and reliable adhesion performance. By setting clear-cut requirements, standards set the level that manufacturers strive to meet, so that adhesives perform as expected in various applications. For example, standards ensure that properties considered for an adhesive are peel strength, shear strength, and durability, so that an end-user gets products suited to his needs while ensuring safety and efficiency.
The standards are especially concerned with peel strength in that they lay down a method of test and provide for measuring the force needed to separate bonded items. This particular measure is important where the adhesive must operate under tension in applications like packaging, construction, and automotive industries: application of the real-life forces as per these standards helps to lessen the failure and build the confidence of consumers.
By encouraging manufacturers to innovate and perfect their formulations and processes, the adoption of standards can indeed spur creativity. An adhesive that conforms to or surpasses a given standard is placed in a favorable competitive position in the market, thereby prompting the entire industry to raise the bar in terms of performance and sustainability. Standards make sure that adhesives must work but should also hold environmental and safety credentials, hence contributing to manufacturers as well as consumers.
Factors Affecting Peel Strength
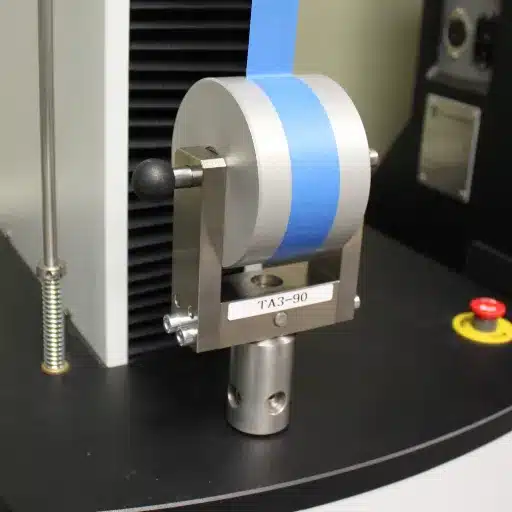
Material Properties Influencing Peel Strength
The first property affecting peel strength would be the adhesive formulation. Viscosities, elasticities, and chemical composition must all be considered when looking at how adhesives resist peeling. In other words, adhesives optimally formulated resist peeling better.
Secondly, the substrates and the manner in which their surfaces are treated have very strong consequences. Clean ones with a smooth texture offer more adhesion than dirty ones with a rough texture. The substrates’ flexibility and material compositions also act against the peeling force of the adhesive layer differently, with some combinations acting well and being more durable.
Last but not least, environmental conditions and treatment processes may impact the peel strength. Factors include temperature, humidity, and exposure to UV rays that get the adhesive properties altered or the bond itself altered through the passing of time. Pre-treatment procedures, such as priming or surface roughening, can aid in adhesion by imparting bonding contact and bond strength, so the adhesive conforms to necessary performance criteria.
Environmental Conditions and Their Impact
Environmental conditions retain significant importance in determining the potential aging and efficacy of adhesive bonds. With fluctuations in the temperature, materials contract or expand, leading to a reduction in their bonding performance with time. At extremely high temperatures, an adhesive may soften and thereby lose its holding capacity. Freezing temperatures may do the crisping job against adhesives. Sudden temperature changes, too, generally increase the stress on the bonded interface causing sudden failure in the worst cases.
Humidity levels have their huge effect on adhesion characteristics. High humidity may lead to moisture accumulation at the bonding surface, thereby interrupting the adhesive from establishing a good bond. Later on, due to this moisture, degradation of the bond may take place, assuming that the adhesive type is not suited to resistant against damp conditions in the first place. On the other hand, low humidity may dry out certain adhesives prematurely before they can be pressed into service.
UV rays are yet other environmental factors that cause breastfeeding to flourish and slowly dissolve some adhesives. Direct sunlight breaks down the chemical structure of adhesives that are not UV-resistant, resulting in a loss of color, flexibility, and bonding strength. The application of a protective coating or the use of an adhesive that is resistant to UV can be considered to avoid such degradation. A glance at the environmental conditions affecting bonded joints and providing appropriate remedies would guarantee the durability and performance of an adhesive system.
Adhesive Formulation and Its Role in Peel Strength
Formulation of adhesives greatly influences peel strength. Peel strength is essentially the force required to separate two surfaces bonded together by peeling, and it is influenced by the chemical composition of the adhesive. Resins, fillers, and plasticizers must be balanced for flexibility and cohesion, which, in turn, affects the property of the adhesive to resist peeling under stress. By manipulating these components, peel strength can be adjusted to meet the requirements of the particular application.
Another factor affecting adhesion would be the nature of the surface material. Depending upon the various conditions during application, surface preparation, such as cleaning and proper priming, assures that the adhesive itself uniformly bonds to ensure high peel strength. Adhesion thus obtained is essential if the application has fluctuating environmental conditions, be it temperature changes or chemical exposures. Other things are choosing a compatible adhesive type, such as pressure-sensitive, heat-activated, or structural, which also contribute further to the performance of the bonded system.
Testing methods, such as the standardized 180-degree or 90-degree peel test, are commonly used to evaluate the peel strength and verify the adhesives for the required specifications. These tests provide relevant data, so one may adjust the formulations of adhesives depending on this data to maintain reliability in various applications automotive assembly to electronic gadgets. With the precise chemistry and surface-compatible binding, the glue may be maintained in respect to peel strength over time; hence ensuring durability and functionality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is peel strength?
A: Peel strength is a term used to denote the force needed to separate two bonded materials; it is usually mentioned in terms of load per unit width of bond line. This measurement is critical with respect to the adhesive strength between two flexible materials or between one flexible material and another type of material.
Q: How is peel strength measured?
A: To measure peel strength, a specific testing setup is used. Particularly, a universal testing machine is normally utilized to apply a perpendicular load onto the bonded materials, averaging the recorded load values along the unit width of the joined materials until complete separation occurs. This will consequently give a tangible demonstration of how well the adhesive performs.
Q: What are the different types of peel tests?
A: Different types of peel tests are performed, such as T-peel and 90-degree peel testing. These tests look at how strong the adhesive bond is at different separating angles or under different conditions, giving an idea of how an adhesive will fare in a specific application.
Q: Why is peel strength essential in material choice?
A: Peel strength is essential in material choice because the adhesion test, peel strength does ensures that an adhesive bond can do its job in suitable applications such as medical packaging or the assembly line. Knowing the peel strength of a particular adhesive ensures that it can withstand the loads and environmental conditions required by the materials.
Q: What influences peel strength?
A: Peel strength is influenced by several factors, including the nature of the adhesive, surface preparation, compatibility of adhesive and adherend materials, and the width of the bond line required. On the contrary, environmental conditions, including temperature and humidity, can affect the strength of an adhesive bond too.
Q: Can you give a brief explanation of the 90-degree peel test procedure?
A: A paint-peel test method consists of preparing samples with the adhesive bonds and placing them into a fixture, itself mounted on a universal testing machine. The machine then applies a load at a certain predetermined angle until the bonding materials separate, which allows for an exact measurement of the adhesive strength.
Q: What is the effect of compression in peel testing?
A: Compression has the effect of influencing peel strength, as it may bear on how well the adhesive can maintain the bond during load. With suitable compression, the curing of the adhesive would have the surfaces in intimate contact, thus strengthening the adhesive bonds.
Q: How do adhesive measurements vary between different materials?
A: Measurements of adhesive strength may vary widely between different materials, since they would differ in surface energy, flexibility, and thickness. These variations need to be accurately accounted for during R&D when trying to develop new adhesive formulations for particular applications.
Q: Significance of the average load per unit width during a peel test?
A: The average load per unit width was significant in that it measured the peel strength of the adhesive bond that existed across the width of the bonding line. This kind of measurement enabled technicians or engineers to uniformly and reliably test the performance of adhesive bonds in many different applications.
References
- Peel Test – TestResources: This source provides details on 180° peel tests and their application in determining bond strength for coatings and adhesives.
- Peel Testing | An Introduction – Instron: Instron offers insights into peel testing methods, including the use of tensile grips and load cells for accurate measurements.
- Peel Strength Test Methods – PLITEK®: PLITEK® discusses various testing methods to evaluate adhesive peel strength for performance and durability.
- Peeling of Flexible Laminates—Determination of Interlayer Strength: This research paper presents a practical peel test setup for flexible laminates, focusing on interlayer strength.
- Analysis of Peel Test – TAPPI: This study explores the relationship between coating thickness and adhesive strength, with a focus on adhesion to porous substrates.