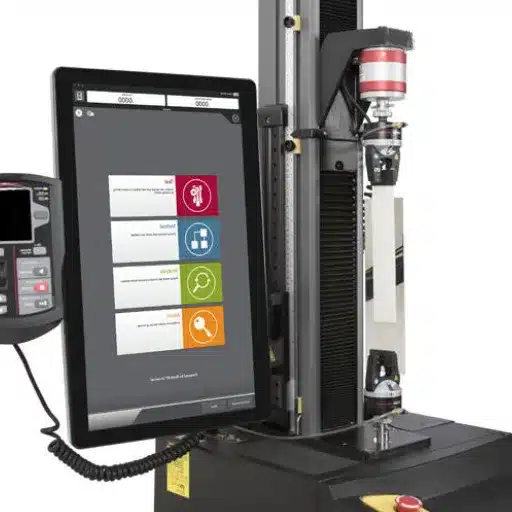
Adhesives act to hold a variety of industries together-from automotive to consumer goods, wherein performance can mean the difference between success and failure. Properly assessing and understanding adhesives for strength, durability, and reliability, guarantee proper functioning, and are considered for long-term performance. This blog briefly enters this intricate world of testing adhesive performance with some attention given to the more familiar peel strength test-a force measurement in which the ability of an adhesive to withstand being pulled apart is determined. By the end of this article, methodologies will clarify, will expound on the theory of adhesion, and will also treat improving adhesion formulations. So, let’s delve into the theory and practical applications that fuel the innovations in the adhesive field.
What is Adhesive Testing and Why is it Important?
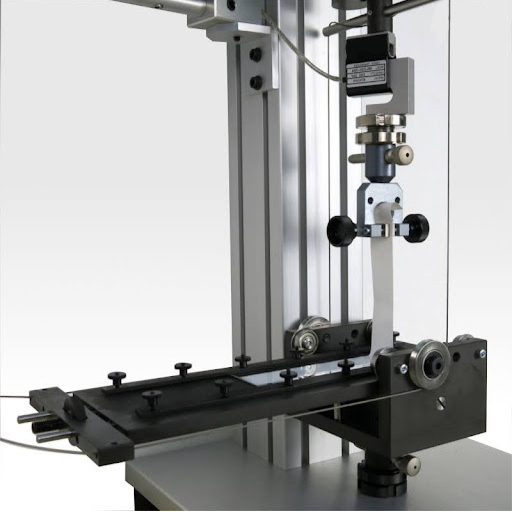

Adhesive tests represent an analysis of performance and durability to determine the effectiveness and quality of adhesives in meeting application requirements. These tests determine the bond strength of adhesives with different substrates, their behavior under environmental influences, and the interaction that may occur with specific substrates. Testing will detect faults, confirming product quality and safety. The safety is essentially warranted in sectors like building, automotive, and healthcare. Knowledge of the adhesive’s working in various situations enables manufacturers to modify formulations, thereby reducing the chances of failure and meeting requirements.
Understanding the Basics of Adhesive Test Methods
Adhesive test methods are performed to measure such qualities as adhesion strength, durability, and performance under conditions specific to the environment or intended use. The commonly used tests are:
1.Peel Tests – A measure of the adhesive’s resistance to peeling forces applied at specified angles, for example, 90° or 180°, that help to determine the bond strength between adhesive and substrate.
2.Shear Tests – Assessing the shear strength of adhesives consists of testing the performance of an adhesive when subjected to a lateral or sliding force imposed by a load, thereby simulating structural forces on an adhesive bond.
3.Tensile Tests – Attempt to pull apart two bonded surfaces to a tension applied to the surfaces to establish and confirm the strength and durability of bonds.
4.Environmental Conditioning Tests – The adhesives would be subjected to extreme temperatures, moisture or chemical environments for a determined period to assess an environmental factor affecting their integrity.
Test standards from ASTM and ISO measure and define methods for providing comparative data on adhesives to help manufacturers in refining adhesive formulations and to satisfy industrial and regulatory standards.
The Role of Adhesive Testing in Product Development
Adhesive testing has a vital function in the application of product development since it allows engineers and manufacturers to check the performance and reliability of materials carrying out adhesion in realistic use conditions. During the development phase, tests measure mechanical properties such as shear, tensile, peel strength, and so forth to be sure that the adhesive withstands the conditions to which it is subjected and thus meets design requirements. Test information may also be used to investigate how adhesives are influenced by certain environmental factors, including temperature changes, UV light exposure, and chemical reactions so that changes may be made to formulations, if necessary.
Identifying potential failure mechanisms at an early stage of development reduces risk and redesign costs, along with speeding up product market entry. It is also important to confirm methods by regulatory bodies and industry standards, especially in the aerospace, automotive, and medical device applications, as well as electronics. Consequently, thorough adhesive testing improves strength, safety, and overall quality of a product that satisfies both manufacturers’ and end users’ expectations.
Key Properties of Adhesives Evaluated During Testing
Adhesive testing aims at key attributes for ensuring the suitability of the material for its application. The primary attributes evaluated are:
1.Bond Strength: It is the ability of an adhesive to hold substrates such that they undergo stress. Factors such as tensile, shear, and peel strength are tested to assess behavior under different kinds of loading.
2.Durability: The adhesives are tested for the duration of their activities subjected to environmental conditions such as humidity, temperature variations, UV exposure, and chemical resistance to determine their reliability in regulation under real circumstances.
3.Viscosity and Cure Time: The flow behavior of adhesives and their occupation period toward body cure is measured, which mainly influences applications and efficiency in production.
4.Thermal and Mechanical Properties: Thermal conductivity, thermal expansion, and mechanical properties, which include the flexibility and toughness of adhesives, are measured in order for those to continue performing under alternate mechanical contractions and temperatures.
5.Aging and Fatigue Resistance: Accelerated aging tests replicate long-term usage in order to assess the capacity of adhesives to endure frequent stresses and/or environmental deterioration as time progresses.
6.Adhesion to Substrates: The tests are applicable in ascertaining its compatibility to different materials intended for bonding. Ensuring proper adhesion eliminates any related complications such as debonding or cohesion failure in application.
What Are the Different Types of Adhesion Tests?
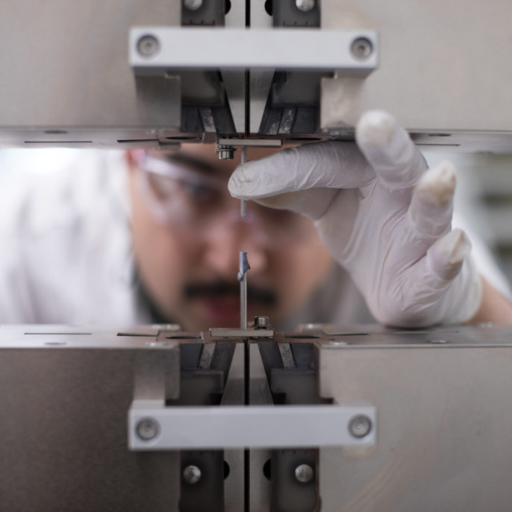

Adhesion tests include peel tests, pull-off tests, shear tests, tensile tests, scratch tests, and tape tests.
|
Test Type |
Purpose |
Key Metric |
Procedure |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Peel Test |
Assess bond |
Peel strength |
Measure force while peeling bonded substrate. |
|
Pull-off Test |
Evaluate adhesion |
Tensile force |
Pull perpendicular to substrate until failure occurs. |
|
Shear Test |
Test sliding bond |
Shear strength |
Apply parallel force to test bonded materials. |
|
Tensile Test |
Measure force |
Tensile strength |
Stretch material directly until failure occurs. |
|
Scratch Test |
Evaluate coating |
Scratch depth |
Apply increasing force to assess resistance. |
|
Tape Test |
Test surface bond |
Adhesion grade |
Apply tape, remove, and measure material retention. |
Understanding Shear Strength and Lap Shear Tests
Shear strength refers to the capacity of heterogeneous matter to resist shearing forces developing across its structure. That is a crucial property when considering materials of bond, especially for construction and industrial uses. One of the most common ways of testing shear strength is the lap shear test. First, two mass materials with an overlap are bonded together, and then a gradually increasing shear force is applied parallel in the plane of adhesion until failure occurs. The highest force applied up to failure is recorded as the shear strength of material. The field conditions are simulated during the test, providing useful information that could be used to determine the strength and integrity of an adhesive or a bonded interface under real stress.
Evaluating Bond Strength Through Tensile Tests
Tensile testing is mainly used for measuring the mechanical bond strength exerted by applying a uniaxial force perpendicular to the bonded interface until failure occurs. It measures tensile adhesion strength, cohesive failure, or adhesive failure of bonds. By finding out the maximum tensile force the bond can withstand, tensile testing gives crucial information about the performance and reliability of adhesives under direct pulling stress. These are used, almost universally, in quality control, research, and development to ensure that bonded materials meet required performance standards within their range of applications.
Peel Tests: Measuring Adhesive Bond Separation
Peel tests evaluate the strength and durability of adhesives when subjected to peeling forces. The peel force that is exerted to separate two bonded materials along a flexible substrate from a general standpoint is measured under controlled conditions, usually at 90 or 180 degrees, in order to mimic real-world peeling scenarios encountered mainly in aerospace, automotive, and packaging industries.
A tensile testing machine applies this testing force: one end of the bonded assembly is clamped while the other is subjected to a controlled peeling force. The recorded data reveal aspects of the adhesive’s peel strength, uniformity of bonding, and failure mechanisms (cohesive failure, which is failure within the adhesive layer, or adhesive failure, which is loss of adhesion between the adhesive and substrate). These measurements are crucial when justifying the choice of adhesives for an application involving resistance to dynamic separating forces.
Peel testing can be adopted in quality assurance systems, ensuring that applied adhesive systems otherwise meet industry-specific standards. Peel tests are usually carried out according to the standards ASTM D3330 or ISO 8510, which describe parameters for test setup, sample preparation, and evaluation of results. By providing measurements that can be used for quantification, these peel tests can assist manufacturers in developing adhesives better suited to enhanced performance and reliability in both test and real-life conditions.
How to Choose the Right Adhesive Testing Machines?
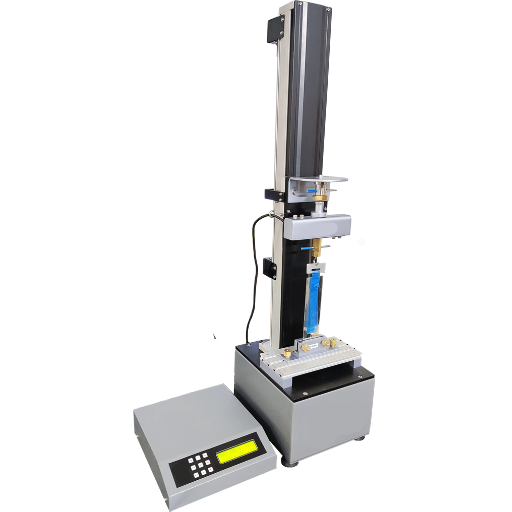

Whenever an adhesive testing machine is selected, certain main points must be considered; such as which specific adhesive properties must be tested: tensile strength, peel strength, shear, etc.; the load capacity which must be applied; and the relevant standards for the tests (ASTM, ISO). Machines should allow a precise control and measurement of the forces applied, including features such as programmable force control and very-high-resolution sensors. Next, consider the compatibility of the machine with various sizes and shapes of adhesive sample, environmental conditions that may be of interest during the testing: temperature, humidity, and so forth. Then, one has to look at how easy the machine is to operate, whether it can be linked to other software packages for data analysis, and finally, ensure the machine meets any regulatory requirements that help in deciding on the machine purchase.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Testing Equipment
1.Load Capacity and Accuracy
Equipment must be able to function under all force ranges that might be applied, while precision in measurements must also be observed. Accuracy and reliability of testing would ensure proper manufacturing procedures.
2.Material Compatibility
The testing equipment should be compatible with the materials under test, i.e., different hardness, elasticity, and composition, with respect to the integrity of materials under tests.
3.Test-Type Compatibility
Confirm that the machine is capable of all the types of tests required by the user, such as tensile, compression, shear, or fatigue testing, and is certificated to perform to industry-accepted standards for each test.
4.Data Acquisition and Measurement Analysis
Good and professional data acquisition and analysis systems and software should be considered for integration, real-time parameter monitoring, and complete analysis.
5.Durability and Maintenance Considerations
One should also consider the durability and service requirements of their test machine: will it be reliable for at least three years and cost-effective with low downtime?
Comparing Various Adhesive Testing Machines
Various adhesive testing machines include tensile testers, peel testers, lap shear testers, tack testers, shear testers, and compression testers.
|
Parameter |
Tensile |
Peel |
Lap Shear |
Tack |
Shear |
Compression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Function |
Pull force |
Peel test |
Bond shear |
Adhesion |
Shear res |
Compression res |
|
Precision |
High |
Medium |
High |
Medium |
High |
Medium |
|
Load Range |
Wide |
Limited |
Wide |
Limited |
Wide |
Wide |
|
Application |
Versatile |
Specific |
Industrial |
R&D |
Industrial |
Industrial |
|
Maintenance |
Medium |
Low |
Medium |
Medium |
High |
Medium |
Ensuring Accurate Results with Proper Calibration
Everything needs to be kept precise so that our results may be accurate. I focus on keeping equipment consistent by following a rigid scheduled calibration program, which involves using certified reference standards and processes per the recommendations of manufacturers or industry standards. Regular calibrations are put in place to minimize measurement deviations and allow measurements to be performed repeatably, thus assuring reliability of the data in various applications. The periodic re-evaluation processes and proper documentation of results also help trace some of the reasons for discrepancies, in case any anomalies or errors occur in the measurements, thereby maintaining a high degree of integrity in operational status.
Why are Adhesive Testing Machines Crucial?
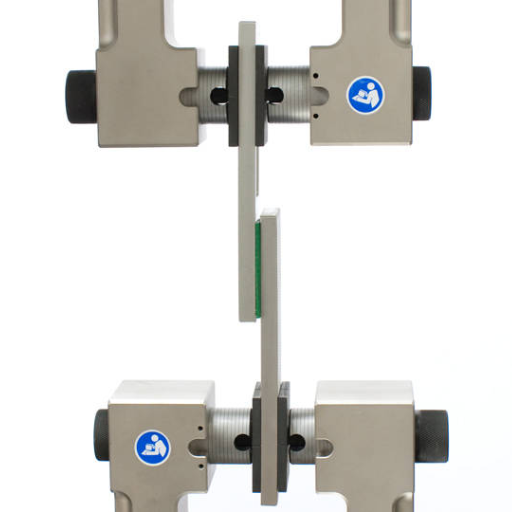
To measure the performance, longevity, and reliability of adhesive materials in all sorts of applications, adhesive testing machines are essential. By checking for tensile strength, shear resistance, or peeling force, this machine will ensure that the adhesives meet the requirements. This information is used by quality assurance teams to address issues in case products are found to contain weak materials or inconsistencies. This is required, especially for end-uses in critical industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. In addition, with standardized tests, these lab-grade machines help in complying with industrial regulations for competitive safety and longer life.
Types of Machines Used for Testing Adhesives
Common machines used for testing adhesives include universal testing machines, peel testers, shear testers, tensile testers, and dynamic mechanical analyzers (DMA).
|
Machine Type |
Purpose |
Key Parameter |
Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Universal Testing |
Tensile, shear |
Tensile strength |
Automotive, Aero |
|
Peel Tester |
Peel force |
Peel strength |
Packaging, Labels |
|
Shear Tester |
Shear stress |
Shear resistance |
Construction |
|
Tensile Tester |
Tension, break |
Load capacity |
Industrial Use |
|
Dynamic Mechanical (DMA) |
Thermal, dynamic |
Modulus, damping |
Research, Polymers |
How to Ensure Accurate Adhesive Test Results?
To ensure accurate adhesive test results, I place importance on three major process areas. Firstly, one has to prepare the materials well and ensure the surfaces are clean, dry, and free of any contaminants, as even the smallest contaminant can interfere with bonding. Secondly, the standard testing procedures like ASTM or ISO should be followed for consistency in measurements. Thirdly, the equipment should be calibrated at regular intervals and operate in controlled environmental conditions in terms of temperature and humidity, thus taking lesser variables into consideration. Following these procedures will maintain the precision and reliability of adhesive testing.
How Do Adhesive Testing Standards Impact Results?

Adhesive testing standards produce an important impact on adhesive testing by providing consistency, reliability, and comparability among evaluations. They implement precise methods, namely, sample preparation, testing conditions, and performance measurements, to minimize variability and thus assure greater reproducibility. By adhering to an established standard testing procedure, one can quantify the working of the adhesives and support claims made of the adhesives in accordance with accepted industry standards.
Exploring ASTM Standards for Adhesive Tests
From the ASTM perspective, numerous important standards are made available so that various performances and properties of adhesives can be tested. The most famous ones are ASTM D1002, ASTM D903, and ASTM D3165.
1.ASTM D1002: This method measures the shear strength of adhesives using single-lap-joint specimens. The test is especially applicable in the context of rigid substrates and therefore facilitates a precise determination of stress upon adhesive bonds.
2.ASTM D903: This method measures peel or stripping strength of adhesive bonds. In most cases, it is applied to determine how well adhesive materials resist separation due to peel forces acting mainly on flexible materials.
3.ASTM D3165: With this method, adhesives’ strength properties are determined within bonded assemblies subjected to generic lap-shear testing, which can be made applicable to a wide array of materials and configurations.
In short, these standards allow testing in a controlled way that yields repeatable, accurate, and relevant results in industrial and research applications, thus helping manufacturers produce adhesive solutions that can be depended upon and accepted on the global stage.
The Importance of Standard Test Method Selection
Choosing a correct test method would mean a valid, comparable, and credible result between test laboratories and for research undertaken in industrial environments. Different test methods are oriented towards particular properties of materials, like tensile strength, bond durability, or shear performance; erroneous selection of a standard could give irrelevant data or misinterpretations. Several factors should be taken into account in the selection: the type of material, environment of application, anticipated loads, and any regulatory requirements. Industry organizations such as ASTM and ISO specify complete standards and offer assurance that any tests performed satisfy technical requirements as well as global standards, assisting in quality assurance, product compatibility, and regulatory approval.
Ensuring Consistency and Reliability in Adhesive Testing
Achieving consistency and reliability in adhesive testing requires adherence to standardized testing procedures coupled with equipment calibration. Following testing regulations of recognized organizations such as ASTM and ISO will generate reports of results that are accurate and replicable. Temperature and humidity are just two examples of the factors that need to be kept under control during tests as they impact the performance parameters of the adhesive. Periodic checking of equipment calibration is recommended as well as continually validating that selected personnel are qualified and competent in performing the testing. Documentation of test results should be structured, cross-referenced against known benchmarks, and used in troubleshooting for improving quality.
Reference Sources
-
Intertek – Adhesive Testing: Provides expert insights and accurate performance adhesive test data for various industries.
-
ICC NTA – Adhesive Performance Testing: Offers accredited adhesive performance testing to validate manufacturers’ findings.
-
Contract Laboratory – Adhesive Testing Guide: A resource for third-party testing labs with expertise in conducting reliable adhesive tests.
-
AMETEK – Peel Strength Testing: Focuses on peel strength testing, explaining its principles and applications.
-
Forgeway – Guide to Adhesive Testing Methods: Discusses various adhesive testing methods, including standards like DIN, ISO, and ASTM.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the peel strength considered important in adhesive performance testing?
A: Peel strength is a significant test because it quantifies the force required to peel an adhesive bond from the substrate. Test results describe the strength and durability of an adhesive joint, especially in the case of flexible materials.
Q: How is lap shear strength tested?
A: Lap shear strength is tested by applying a tensile force parallel and in the direction of the adhesive bonds until failure occurs. Besides testing the strength properties, this test method helps to understand the capacity of adhesive joints to bear loads, primarily important in the domain of structural adhesives and wood adhesives.
Q: How would the presence of coatings affect the adhesive performance?
A: Coatings may either aid or hamper adhesive properties depending on their make, first, and on the treatment application. Testing the compatibility of coatings and adhesives becomes an important step to ensure that the coatings will not hinder adhesive performance nor confound strength testing results.
Q: Why is the testing of PSAs valuable?
A: The pressure sensitive adhesives are valuable for applications in which immediate bond strength is attained on contact. Testing of these adhesives refers to resistance of adhesive under certain conditions between two rigid substrates.
Q: What are standard test methods to assess strength properties of adhesives?
A: Tensile, peel, and shear constitute the standard test methods for the assessment of strength properties. These methods are used in the investigation of mechanical properties of adhesives in accordance with shear and their applicability for certain substrates such as wood products or structural applications.
Q: How does the adhesive bond’s shear strength influence its performance?
A: Shear strength of adhesive bonds plays an important role in determining an adhesive’s ability to endure forces applied parallel to the bond line. High shear strength in simple words means an adhesive withbc strong bond; hence such adhesives are useful in processes that require application of huge load.
Q: How important are adhesive shear tests by tension loading?
A: The significance of an adhesive in shear tests by tension loading is given by providing information on the state of stress applied to adhesives. This kind of test is significant for evaluating adhesive behavior in real applications, especially in dynamic loading.
Q: Why does a standard specification for adhesives matter?
A: A standard specification for adhesives provides assurance of consistent and hence reliable performance for adhesives in application. The specification covers the testing of adhesives to ensure products meet regulatory safety and quality levels.
Q: How are adhesive shear bonds different from other types of bonds?
A: Adhesive bonds in shear are subjected to forces applied parallel to the bond line rather than tensile forces or peel forces. Thus, these bonds are suitable in situations where shear strength is the most significant parameter, such as in structural elements bonded by adhesive.
Q: What are the factors affecting the test method for apparent shear strength?
A: The factors from which the test method for apparent shear strength depends include the type of adhesive, substrate materials, environmental conditions, and the particular application requirements. There shall be an understanding of these to choose the proper test method to genuinely measure the performance of the adhesive concerned.






