When it comes to evaluating the quality and durability of materials or adhesive bonds, peel strength testing plays a critical role. Whether you’re working in manufacturing, product design, or quality assurance, understanding the importance of peel testing can lead to stronger products and better performance outcomes. This guide will explore the fundamentals of peel strength tests, clarify their purpose, and outline various methods used across industries. By the end of this article, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how peel tests work, why they matter, and how they help ensure reliability and quality in countless applications.
Introduction to Peel Strength Testing
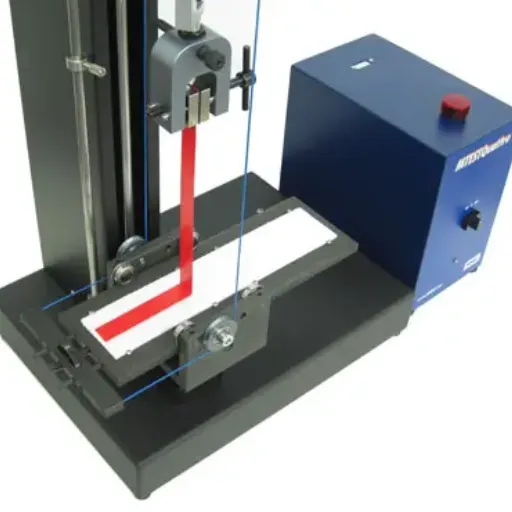
Definition of Peel Strength Test
A peel strength test is a method to measure the force needed to pull apart two bonded materials. This test is usually used to assess the durability and reliability of adhesives, tapes, laminates, or other such bonding agents. Peel testing quantifies the bond strength under set conditions and, thereby, imparts data about the performance and appropriateness of an adhesive in a given application.
Usually, for the test, a material is pulled away at some standard angle- mostly 90 or 180 degrees-from the other to gauge how much force is needed to break the bond so manufacturers and researchers can thus consider adhesion, resistance to the environment, consistency, and anything ofin relation. These are matters that are even more important to industries like automotive, aerospace, packaging, and electronics, where materials, once bonded, will have to withstand rigorous requirements.
These kinds of testing-measuring peel strength will enable ensuring that the products are safe, functioning, and worthy of an ever-growing lifetime. By detecting inconsistencies in adhesive behavior or weaknesses, the tests offer a way to improve the material quality or properties. This eventually leads to more satisfactory products and thus enhance consumer confidence in the durability and reliability of their applications.
Importance of Peel Strength in Adhesive Applications
Peel strength is an important measurement of an adhesive when it is able to resist the forces trying to separate the bonded materials. This measurement makes a great deal of difference in how a product performs and how durable it is in real-world applications. Weak peel strength would cause premature bonding failures that would compromise the integrity of the product and pose potential safety issues.
Once the peel strength is ensured, manufacturers can further improve product reliability and service life. Obviously, the elastics having the highest peel strength provide the best function and durability to the product, so they have shown a potential for high-stress applications in the automotive, aerospace, packaging, and construction trades. These industries are a bit harsh for the adhesives to withstand a peel test examination since adhesives should be capable of withstanding plenty of wear.
Knowing peel strength is also very helpful in selecting materials and adjusting processing parameters, as well as for development and design. Based on an intense study, various adhesives undergo modifications so that they meet all standards in almost any application, which in turn comes out as the best outcome. With this important assurance of peel strength, manufacturers win consumer confidence in that their product will perform effectively under almost every conceivable condition.
Overview of Test Methods
There are various types of approaches with which to test adhesives for strength, durability, and application suitability, so that adhesives can be appropriately qualified with respect to their quality and performance standards. The peel test is one of the commonly adopted tests, as it analyzes how adhesives can withstand bonding of two surfaces under different stress conditions. This test method is very important, since it simulates the real-life situations to which adhesives need to perform and returns critical information about adhesive performance under bending or pulling forces.
The other test method is shear testing, which checks the sliding resistance of adhesive layers. This is highly relevant for uses where materials have to bear heavy loads or movements frequently. It aids manufacturers in deciding the failure limit of adhesives so that the product can be used safely under heavy environment conditions.
Also, environmental tests check glue performance when subjected to temperature variations, humidity, or chemicals. These tests forecast the durability and aging of an adhesive condition under different environments, hence confirming that the adhesive can work in any stipulated time. The very combination of test methods gives the possibility for manufacturers to develop top-grade products with assured performance and safety.
Industry Standards for Peel Strength Testing
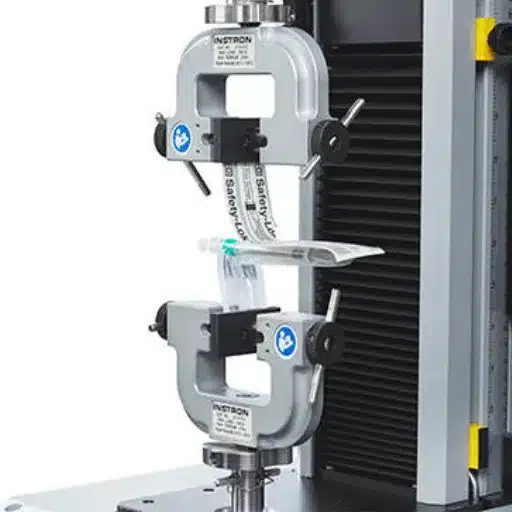

Overview of ASTM D1876
In the ASTM D1876 test, more commonly referred to as the T-Peel Test, peel strength for adhesive bonds between two flexible substrates is determined. The peel force generated is the force needed to progressively pull two substrates apart under specific conditions. The function of this test is crucial in safety and reliability assessments of adhesives in aerospace, automotive, and packaging industries.
The test is conducted by placing a specimen prepared with bonded flexible materials in a testing machine. It is then subjected to a tensile force that peels the layers apart at a constant rate, normally 25.4 cm/min (10 in/min). The measured force, required to peel and separate the layers, is then averaged over the width of the bond line. The entire set of procedures is standardized to allow for use in particular applications and under varying environmental conditions, hereby guaranteeing valid results.
A big significance behind ASTM D1876 is its assistance to manufacturers in assuring the performance of adhesives on stress. With clear specifications on preparing samples for testing, testing conditions, analysis, and presentation of test data, this standard helps in the development and evaluation of products to meet the needs of adhesives under particular applications. This testing scheme further contributes extensively to the development of bonding technologies and securing industries.
ISO Standards for Adhesive Testing
ISO standards for adhesive testing ensure that products meet stipulated guarantees of quality and reliability. They are a yardstick for the assessment of adhesives in varying contexts so that the manufacturers can maximize their potential to satisfy different industry requirements. The standard includes a series of guidelines concerning the preparation of test samples, testing procedures, and data analyses so that adhesives meet the intended needs for a specific application.
On a very fundamental level, these standards maintain the integrity of the global marketplace, enforcing compatibility and reliability across industries. They create a healthy environment for comparisons between products and collaboration amongst manufacturers towards common testing grounds. Adherence to the ISO standards also maintains consumer and business confidence in the adhesives meeting their respective benchmarks of quality and safety.
Beyond these, ISO standards for adhesive testing become an engine for innovation by pushing the need for advanced bonding technologies. The manufacturers utilize these rigorous test standards to refine their formulas, develop longer-lasting products, and introduce new solutions to the market. This ensures the sustainable growth of the industry while guaranteeing efficient and long-term performance.
Importance of Adhering to Test Standards
The importance of test standards lies in the ability to ensure reliability, safety, and performance in adhesive products. These standards provide test methods concerning uniformity to make sure that all products qualify to meet various industry and regulatory requirements. Thus, following these guidelines helps manufacturers and suppliers to produce trustworthy and efficient solutions while minimizing product failure or defects.
Another important reason for complying with the test standards is to facilitate international trade and compatibility. These standards act as a universal language for assessing adhesive properties and enable manufacturers to confidently market their products internationally. Thus, adherence fosters cross-border collaborations and maintains that adhesive products stand up to the expectations of diverse industries, within any given location.
Test standards are also catalysts promoting innovation and sustainability. Being pushed by tight confines holds manufacturers to improve their process and improvement in material toward the production of adhesives that are good for the environment and perform well. Trusting these standards itself contributes to the industry in building trust for the long-term development as well as in environmental and safety concerns.
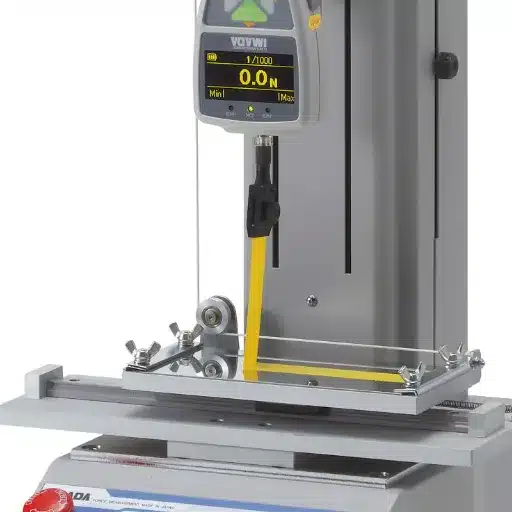
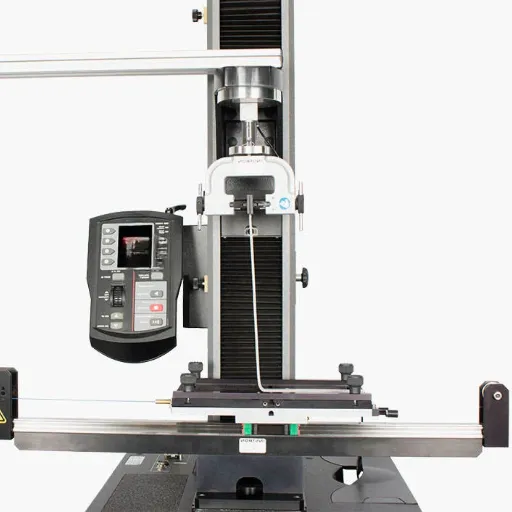
Equipment Used in Peel Strength Testing
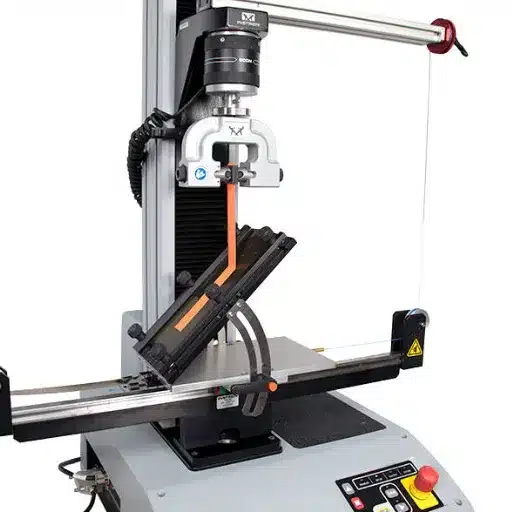

Universal Testing Machine Overview
The Universal Testing Machine is one of the versatile pieces of equipment for evaluating the mechanical properties of materials under different conditions. It is designed for wide-ranging tests such as tensile testing, compression testing, or peeling strength testing; hence it becomes essential to assure the quality of a product or carry out research in many fields. The machine applies a force to the specimen in a controlled manner and also measures how much deformation takes place until failure, thus giving valuable information on the performance of the material.
The major parts of the UTM include a load frame, crosshead, load cell, and testing grips. The load frame forms the main frame structure, whereas the crosshead travels, applying force on the test specimen. The load cell is used to measure the force so applied to ensure accuracy. The grips or fixtures hold the specimens firmly during testing, with interchangeable fixtures enabling the machine to be adapted to various forms of testing. This versatility allows for testing of a wide range of materials, from metals and polymers to adhesives and textiles.
Thus, the paramount advantage of a UTM in terms of material testing lies in offering constant and reproducible results, upon which basis one can evaluate a material with confidence. The ATM has a standardized procedure that adheres to international testing standards, for instance, ASTM or ISO standards. The machine acts as a healer, giving all the information on properties and performance of materials, being applied in research and further development as well as quality control in the building, aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries.
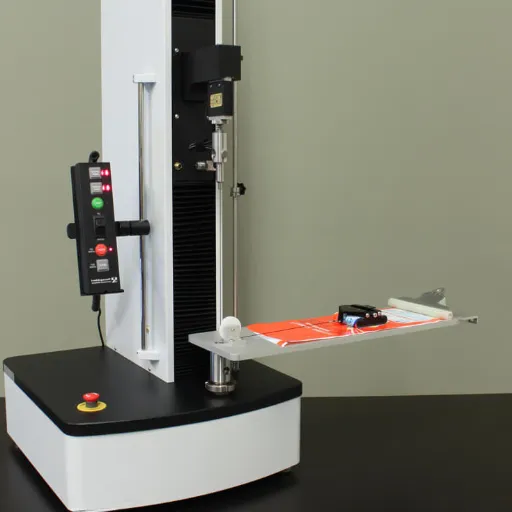
Specific Peel Testers and Their Features
Peel testers are highly sensitive instruments that are used to determine the adhesive strength or bonding performance of materials, depending on certain controlled conditions. Usually, they test how much force is required to peel a material A from material B; an important factor in maintaining the reliability of products in industries such as electronics, packaging, and manufacturing. Moreover, a major feature of peel testers is that they ensure repeatable testing by offering a constant speed and angle during the testing. This is vital to achieve comparable results.
The more modern peel testers contain adjustable settings for different types of tests like 90-degree and 180-degree peeling. This allows for a better simulation of real-world applications. Many peel testers are also equipped with a state-of-the-art digital interface that shows forces in real-time and saves this information for later analysis. This assists in closely tracking the performance of adhesives, films, and laminates under differing conditions and material specifications.
Another major feature has to do with standard testing protocols such as described by ASTM or ISO standards, as these allow the results to be trustworthy and worldwide benchmarking to be met. Peel testers are useful in industries like packaging, automotive, and aerospace and are primarily used for quality control, research, and development work. Their design allows easy access to testing materials, making these machines an essential tool in both the laboratory and production environments.
Calibration and Maintenance of Testing Equipment
Testing equipment must be regularly calibrated and maintained to ensure that the testing process remains accurate, consistent, and reliable. Calibration basically comprises of checking the performance of an equipment versus an accepted standard. This allows the determination of any deviation so as to ensure that the equipment is providing accurate measurements. An annual calibration is generally recommended by testing codes, or more frequently depending on the intensity of use of the equipment and the level of accuracy required.
For maintenance, it is important to keep equipment in a genuine working condition and to prolong its life. Maintenance consists of cleaning, checking for wear and damage, and seeing that all parts move properly. For example, in the case of mechanical units, lubrication may be necessary; whereas, with electrical units, it will be fault finding. Preventive maintenance keeps the equipment away from failures and reduces the expenses of downtime.
The calibration and maintenance should be done either by competent personnel or according to the instructions of the manufacturer. Also, keeping records of all calibration and maintenance activity is helpful in tracing the history of the equipment and helps in meeting the requirements of the industry. Applying such practices will help to ensure the integrity of their testing process and hence consistent high-quality results.
Factors Influencing Peel Strength Test Results

Adhesive material properties are paramount to peel strength testing results. The important considerations are the adhesive type, chemical makeup, and bonding mechanism. For example, some adhesives are designed to bond more firmly with a given substrate, which could contribute to a higher peel strength reading. Additionally, the adhesive’s viscosity and curing conditions will determine how well it can spread on and stick to the surfaces being tested.
Another important property is adhesive elasticity/flexibility. By this, highly elastic adhesives will absorb stress during the peel test and thus show higher values of peel strength. In contrast, some brittle adhesives may possess lower peel strength as they cannot undergo much deformation before they fracture. This behavior underscores the necessity for careful application-dependent selection of adhesives.
Other factors affecting peel strength measurements are related to environmental changes affecting the properties of the adhesive material. An alternative set of temperature, humidity, and chemical exposure can bring about a change in the adhesive’s performance. For instance, a particular adhesive may soften at high temperatures, decreasing the peel strength, while low-temperature ground conditions may harden it to a powdery state. A good insight into the material-specific properties ensures proper testing for prediction concerning a diverse set of conditions.
Surface Preparation and Treatment
Proper surface preparation represents one of the critical factors for the success of adhesive bonding. Surfaces must be clean and dry, while or in the absence of any contaminants such as grease, oil, or dust, which compromises the adhesive bond. Cleaning may be by means of solvents, detergents, or abrasive procedures, depending on the material involved. Of great importance to the adhesion is the smoothness of the surface and its being properly prepared; good adhesion will ensure long life, while adhesion failure may occur prematurely.
After cleaning, surface preparation may usually include mechanical or chemical treatment-likely surface abrasion or acid-etching-to modify the surface roughness and/or alter the chemical properties of the material. The treatment provides a good surface for the adhesive to interact with, thus raising the durability and performance of the bond. The treatment to be selected depends on the material to be bonded and the kind of the adhesive, so that the two are compatible.
Finally, there may exist applications in which priming of the surface improves bonding. Primers are intermediate coatings generally intended to promote adhesion, but they also protect the material from such external influences as moisture and corrosion. Hence, thorough preparation before applying any adhesives, during which time the workmanship will apply, is the key to creating reliable and long-lasting bonds even under harsh circumstances.
Environmental Conditions During Testing
During testing, the environmental conditions play an essential role in determining the performance and reliability of an adhesive. Depending on the type of adhesive, factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to UV radiation directly affect their properties and bonding capacity. One must try to mimic the exact operating condition during the testing phase, thereby getting a clear idea about the actual durability and performance of the adhesive.
Due to release or increase in temperature, adhesives may contract or expand, respectively, and a time-dependent weakening of the bond may set in. Adhesives soften at high temperatures, weakening the bond strength, whereas low temperatures tend to harden an adhesive making it prone to cracks. Testing should take into account the entire temperature range to which an adhesive is to be subjected in actual application situations so as to guarantee its long-term reliability.
Humidity and moisture also play great roles in adhesive performance. In the presence of moisture beyond certain levels, some adhesives undergo chemical degradation and loss of adhesion, especially if they are not water-resistant. Testing must include simulated conditions of high and low humidity to evaluate moisture exposure resistance. Addressing these environmental factors during testing ensures manufacturers know the performance criteria that their products must meet in real-world applications.
Best Practices for Conducting a Peel Strength Test

Steps for Accurate Test Execution
- Prepare the Materials and Equipment: Begin by collecting all necessary materials, including the respective adhesive specimens and substrates for testing. The substrates need to be cleaned and degreased to get precise bonding results. Value correct calibration of the peel strength testing machine as per the manufacturer’s manual to make measurement accurate.
- Carry Out Test Under Controlled Condition: Put the test in at the controlled atmosphere since external variables such as temperature or atmospheric humidity might influence the results. Fix the adhesive specimen into the specimen fixer properly, and keep the substrate in the testing device. Observe the specified test conditions, such as peeling angle and speed, which are generally 90° or 180° angular rate with a constant speed for meaningful results.
- Record and Analyze Results: Record the test force for the peeling process as displayed on the peel testing equipment. Organize the data into a clear form and analyze it to give the performance rating of the adhesive such as maximum strength and behavior under stress, which can then be compared with the standards of the industry or product specification to gauge if the adhesive meets desired performance levels.
Interpreting Peel Test Results
Peel test results give significant hints about the adhesive’s behavior when subjected to stress and its strength. The main result to check is the maximum peeling strength, which tells the amount of force the adhesive can sustain before it separates from the surface to which it is glued. The higher the value, the better the adhesion.
Lower range irregularity and sudden drops of force pointed out during the stress phase might correct concern for uneven application or intentional weak bond areas. One must observe the deterioration behavior under stress: is it uniform and at a relatively constant force? Analyzing these behaviors helps in pinpointing any potential defects of the adhesive, or factors that are detrimental to its reliability.
Results have to be evaluated in accordance with industry standards or agreed product specifications to find if the adhesive granted the expected performance level. Standards specify minimum acceptable strength and durability to ascertain that application in the appropriate field is feasible. Interpretation in-if-a-proper-way-will-ensure-greatly-reliable-decisions-for-product-development-and-quality-control.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Surface preparation is a common pitfall in adhesive applications. Any dirt, grease, moisture, or surface irregularities can greatly reduce the strength of the adhesion and its durability. To avoid this, one must make sure that surfaces are cleaned, dried, and treated according to the adhesive’s instructions. Sanding, degreasing, or applying a primer can contribute to better adhesion since these methods create a more receptive surface environment.
Choosing the wrong type of adhesive for a specific use is another frequent problem, which likewise will result in failure. To prevent this, one must study all the specifications of an adhesive very carefully, paying special attention to bonding capabilities, temperature ranges, or resistance to a certain environment. To be able to make a good choice, the information from the data sheets and industry standards must be taken into consideration.
Improper curing is the final pitfall that greatly affects the performance of the adhesive. Many adhesives need to cure for exact times or under exact conditions to reach their full strength. If a bond is rushed, it is not apt to come to full strength and stability. Thus, never depart from the curing directions, including heating, pressure, and time. It pays to have small pieces tested to ensure that the adhesive really works well before full application.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a peel strength test?
A: Peel strength is a mechanical test that helps to determine the adhesive strength of materials in terms of the force applied to peel apart bonded surfaces. Essentially, a force per unit width is applied to a sample to determine the peel adhesion and resistance of the adhesive bonds.
Q: What are the various peel tests that can be performed?
A: These include the 90° peel test, 180° peel test, climbing drum peel test, and variable angle peel test. Each type provides a measure of peel resistance and the strength of adhesion at various angles, offering key insights into how adhesive bonds fare in different real-world applications.
Q: How is the 180° peel test conducted?
A: The 180° peel test is performed by bonding two materials and then peeling the two apart at a 180-degree angle. It is a good way to measure adhesion strength of adhesive bonds and the peel adhesion of pressure-sensitive adhesives.
Q: What factors affect the peel strength of adhesives?
A: Factors affecting the peel strength of adhesives include the choice of adhesive, surface preparation of the substrates, conditions and rate of peel. Also important are the strength of the adhesive bond and the resistance to peeling of the adhesive bonds.
Q: What is needed to perform a peel strength test?
A: Thin test specimens are peeled from the testing equipment. The most common configuration is a test frame, usually universal testing machine, with a test fixture to hold the specimens and the appropriate test samples. The test fixture configuration is crucial to accurately measure the peel force exerted per unit width.
Q: What is meant by peel resistance?
A: Peel resistance is the maximum force of separation per unit width that the adhesive in the bonded system can resist without failure. It is one of the parameters determining peel strength and reflects the durability of the bond under tension.
Q: How can one measure the peel strength of an adhesive?
A: Peel strength determination involves separating a specimen with controlled peeling force and recording the maximum force of separation of the bonds. Using this, the peel strength can be calculated as force per unit width.
Q: What is the climbing drum peel test important for?
A: The climbing drum peel test is important because it simulates practical conditions where adhesive bonds may be subjected to dynamic loads. Data derived from this method shall be important in analysing peel resistance and adhesion performance of adhesives under conditions of movement or stress.
Q: Can this peel strength test be conducted for assemblies of flexible-bonded-to-rigid test specimens?
A: Yes. This peel strength test can be employed for flexible-bonded-to-rigid test specimen assemblies. This kind of test aids in measuring adhesion strength and peel resistance of adhesives used in applications involving both flexible and rigid materials.
References
- Peel Test – TestResources – An overview of 180° peel tests to determine the bond strength of coatings and adhesives.
- Peel Testing | An Introduction – Instron – A detailed introduction to peel testing, including equipment and methods.
- Peel Tester: How Does It Work, How To Test – Xometry – Insights into how peel testing ensures adhesive bonds meet strength standards.
- Standard Test Method for Peel Resistance of Adhesives – ASTM – Information on ASTM standards for determining peel resistance of adhesive bonds.
- ASTM D903 Peel Adhesive Testing – DDL, Inc. – Details on ASTM D903 and other standards for testing adhesive bond strength.







