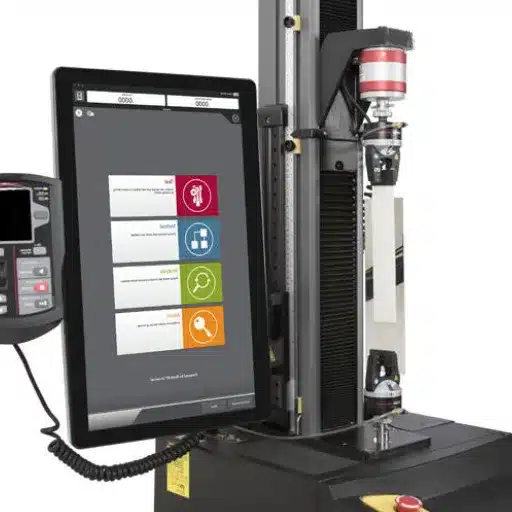
Introduction to Peel Strength Testing
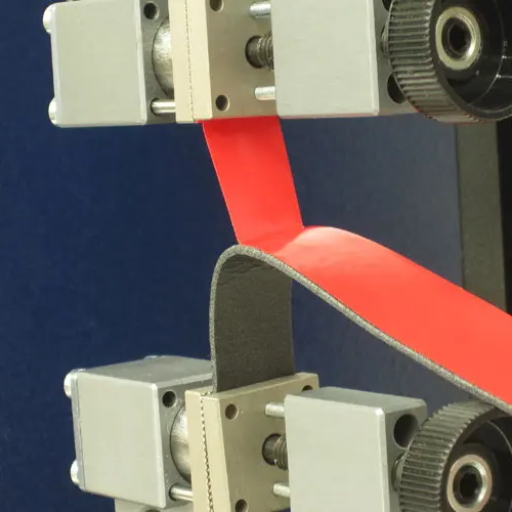
Peel strength testing measures the force needed to separate two bonded materials by applying a stress at a specific angle, commonly 180 or 90 degrees. This method is fundamental in evaluating the adhesive’s capacity to withstand tensile and shear forces during usage. By simulating actual conditions, peel strength testing provides accurate information concerning bond strength and consistency. The data are utilized in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and packaging, to support product standardization in terms of performance and safety.
What is Peel Strength?
It states the force required to separate two bonded materials by peeling at a specified angle, e.g., 180 or 90 degrees. This parameter is crucial for evaluating the durability and reliability of adhesive bonds under stressful conditions. Recent data on Google Trends reveal an increase in interest in peel strength over the past few years from various industries, likely due to recent developments in adhesive technologies. The factors affecting peel strength include the type of adhesive, surface polishing, bond thickness, temperature, and humidity. High peel strength may be considered an advantage where reliable performance under dynamic loads is necessary, such as automotive vehicle design, aerospace engineering, and medical device manufacturing. Accurate measurements of peel strength will help engineers predict and improve material performance, refine bonding methods, and comply with rigorous standards for safety and quality.
Importance of Peel Strength Tests
Peel strength tests are crucial for evaluating and assessing the integrity and durability of adhesive bonds across various industries. Such a test measures the force required to peel one product from another, providing vital information to ensure product reliability and safety in use. High peel strength indicates that an adhesive can withstand mechanical stresses, temperature fluctuations, and humidity. Hence, the test is used in various sectors such as the automobile, aerospace, and electronics where adhesives replace conventional fasteners.
With peel strength tests, manufacturers can determine whether a given adhesive bond is of good quality during product development and in quality assurance. Such data enable engineers to identify weak points in the bond, improve adhesive formulations, and modify application methods for use with specific materials and under particular working conditions. These tests have applications ranging from structural bonding to microelectronic assemblies and serve as a guarantee that manufacturers conform to strict standards, decrease the risk of product failures, and ensure enhanced performance in the long run. Such a measure is crucial for ensuring both safety and customer satisfaction in this highly regulated industry.
Overview of ASTM Standards
ASTM International, formerly known as the American Society for Testing and Materials, develops and publishes internationally recognized technical standards for nearly every industrial sector. The standards, which number over 12,500, encompass testing, classification, and performance standards for materials, products, systems, and services. The standards most relevant to our purposes specify the properties of materials, standardize test methods, and establish criteria against which products are measured for reliability and regulatory compliance. The construction, aerospace, healthcare, and manufacturing industries particularly utilize ASTM standards to sustain consistency, improve quality, and meet the rigorous requirements of heavy industry. Scientists, engineers, and other industry specialists collaborate in developing and updating standards, ensuring that these standards remain relevant to current technologies and challenges.
Key ASTM Standards for Peel Strength Testing
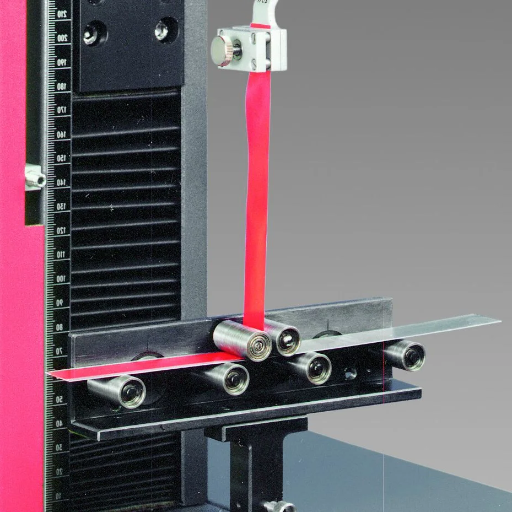
Several ASTM standards are essential for peel strength, allowing materials and adhesives to incorporate specific requirements into their testing procedures for performance under imposed conditions. Included are:
ASTM D903
It describes the peel or stripping strength of adhesive bonds. Mainly, it is used in flexible bonded assemblies with strict conditions laid down for the test, such as peel rate and angles.
ASTM D1876
Commonly referred to as the T-Peel Test, this standard measures the adhesive strength of joints between flexible materials. Hence, it provides a basic criterion for estimating the performance of bonds on laminated or coated structures.
ASTM D3330
This test method covers peel adhesion of pressure-sensitive tapes to ensure uniform adhesive strength in industrial and commercial applications.
The standards constitute a test protocol, specify the equipment to be used, and outline the method of data analysis, thus ensuring a reliable basis for stipulating test methods in accordance with the material requirements. While a quality judgment will be made on a matter of good practice, conformance with these standards will show that test methods used are fair and justifiable.
ASTM D1876: Standard Test Method for Peel
The ASTM D1876 standards, also known as the “T-Peel Test,” constitute a widely accepted procedure used to investigate the adhesive or bonding strength of flexible materials joined by an adhesive film. This procedure directly relates to polymer films, thin sheets of metal, or textiles, where the industry promotes the strength of bonds.
It measures the force required to peel the two bonded materials apart under T configuration at relatively controlled conditions. The T-Peel test is conducted in a tensile testing machine equipped with specialized grips to secure the sample. The results are reported in terms of average peel strength per unit width (e.g., pounds per inch or newtons per meter). This test procedure is necessary to ensure that the adhesives meet the requirements of applications where environmental conditions are unsuitable, such as those in aerospace or automotive industries.
ASTM D903: Peel Adhesion Test Method
ASTM D903 prescribes a standardized method for finding the peel or stripping strength of adhesive bonds between flexible and rigid materials. The technique involves evaluating the peeling force of bonded materials, where the flexible substrate is peeled at an angle of 180°. This standard is commonly used in the packaging, automotive, and aerospace sectors to maintain consistent conditions for sample preparation, peeling speed, and other factors, thereby obtaining reliable and reproducible results. ASTM D903 provides a technical evaluation of adhesive performance in applications involving laminates, tape, and pressure-sensitive adhesives, enabling critical decisions on bond durability in relation to horticultural or industrial environments.
ASTM D3330: Peel Resistance Testing
ASTM D3330 provides a well-recognized standard test method for determining the peel adhesion of pressure-sensitive tapes. The test measures the force necessary to peel the tape at 180° angle from the standard substrate. By controlling all variables, such as the rate of peeling, the method of substrate preparation, and environmental conditions, repeatability and consistent measurements are maintained, which are essential for quality assurance. The outcome of this testing provides a benchmark for adhesive strength and durability, enabling producers to enhance tape performance in various applications, including packaging, medical devices, and electronics.
Testing Methods and Equipment
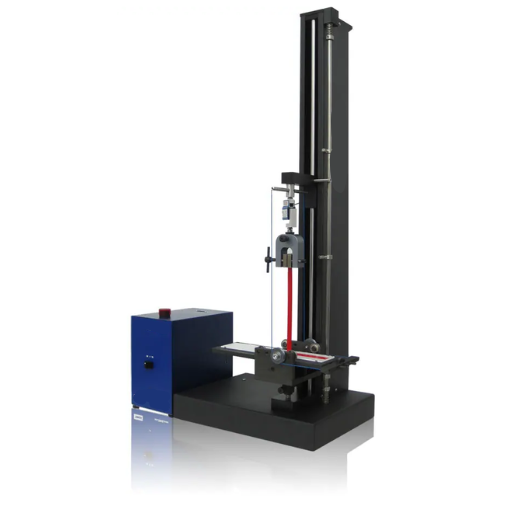

Peel strength testing instruments are specifically designed to provide optimal measurements. Tensile testing machines with fixtures for peel testing are commonly used. The test sample is mounted inside the fixture of the peel testing machine in such a way that it will align with the sample and correspond to the test at measurement so as to diminish any deviation from lateral forces during the test. Then the testing machine applies the desired force to detach the sample from the surface at a predetermined speed, usually prescribed within the test method standards, such as ASTM D3330 or ISO 8510.
Parameters such as peel angle (typically 90 or 180 degrees), separation speed, and sample preparation are all strictly controlled to ensure consistency and reproducibility. Several tests may be conducted in environmental chambers where the temperature and humidity are controlled, as these environmental factors significantly influence adhesive performance. High-precision data acquisition systems are integrated with the testing machines to accurately record force-displacement curves, enabling the analysis of the mechanical behavior of the adhesive. This analysis includes the maximum peel force, average peel strength, and failure modes.
Common Peel Strength Test Methods
- T-Peel Test: This type is implemented in peeling the two flexible adherends apart with the T-configuration. It evaluates adhesive bond strength and, consequently, the behavior of the adhesive under peeling forces.
- 90-Degree Peel Test: In this method, a flexible adherend is repeatedly peeled away from a rigid substrate at a constant 90° angle. Since the set geometry remains fixed throughout testing, it is traditionally used to evaluate the adhesive bond between flexible and rigid materials.
- 180-Degree Peel Test: The 180-degree test measures peel force between a flexible material and a rigid or flexible substrate at a constant angle of 180 degrees. The method is mainly used for tape-based adhesives and adhesives for film applications.
- Floating roller peel test: To maintain a constant peel geometry and decrease stress build-ups during the test, this method uses a floating roller and is used for testing bonds between a flexible and metallic adherend.
- Cleave Test: When performed on rigid or semi-rigid substrates, this test gives information about the adhesive’s response to forces applied in a prying motion and also allows for assessing bond strength under non-peeling loads.
Equipment Used in Peel Testing
Peel testing needs precise, highly specialized equipment so as to ensure that the tests are accurate and yield reproducible results. In general, these consist of:
| Equipment Type | Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Universal Testing Machines (UTM) | Provide controlled loading conditions and measure force/displacement | Programmable, variable test parameters, high accuracy |
| Peel Test Fixtures and Jigs | Maintain constant test geometry | Secure specimen holding, consistent peel angles (90° or 180°) |
| Load Cells | Measure peel force with high precision | High accuracy, real-time force measurement |
| Environmental Chambers | Control temperature and humidity conditions | Simulate real-world environmental stresses |
| Data Acquisition Systems | Record and analyze test results | Real-time data recording, force-displacement curves |
These types of equipment work together to ensure that all peel tests are carried out using standard methodologies and to provide results that are reliable and trustworthy.
Setting Up for a Peel Strength Test
The following are some key steps one needs to go through to get a proper setup of the peel strength test:
- Sample Preparation: Samples for testing must meet specific requirements in terms of dimensions, bonding surfaces, and alignment. Both surfaces should be cleaned to remove any contamination that can inhibit consistent bonding.
- Test apparatus configuration: The peel testing machine should be calibrated and configured according to the relevant standards, such as ASTM D903 or ISO 8510-2. The peel angle is commonly set at 90° or 180°, depending on the test method used. Sample specimens should be gripped securely to avoid slippage during testing.
- Environmental Control: Keep test trials under controlled temperature and humidity, as variance in environment can cause divergence in test outcomes, while adhesive properties are dependent on the environment.
- Data Acquisition Setup: The data recording system should be verified to ensure it is operational and configured to record force-displacement curves and other relevant metrics, meeting the requirements specified in the test set.
When all of the above criteria are fulfilled, then the test setup will surely produce reliable and repeatable results, leading to an accurate assessment of peel strength.
Applications of Peel Strength Testing Across Industries
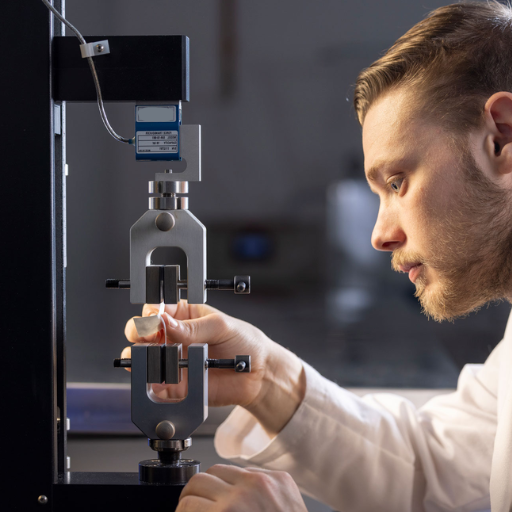

Peel strength testing has applications in numerous industries to evaluate the performance of adhesives under varying conditions. These tests in the aerospace and automotive industry ensure reliability in adherence of components while being subjected to mechanical stresses or environmental fluctuations. The packaging industry performs peel strength testing to assess the integrity of seals and adhesives used on consumer products. This ensures that the product is safe for handling and has an adequate shelf life. Likewise, such tests assure the attachment strength of thin-film electronics, laminates, and components to new surfaces or against heat and pressure. In medicine, peel tests serve as an assurance of the proper adhesion of sterile packaging and, by extension, the medical devices themselves. Generally, in the whole kerfuffle of assurance, peel testing appears mto be ajorly representative of the building blocks of quality, safety, and performance.
Packaging Industry
The packaging industry utilizes peel testing to assess the degree of strength for seals, adhesives, and materials used in packaging systems. It is expected to assure that the packages will retain their integrity throughout transportation, storage, and consumer handling. The key applications include seal strength testing of flexible packaging, adhesion testing of laminated films, and evaluation of tamper-evident packaging for safety purposes. In analyzing these aspects, peel testing thus sustains the standards for protection, shelf life, and consumer safety.
Electronics and Adhesive Bonding
Peel strength testing is essential in electronics and adhesive bonding to ensure reliability and performance under various operational conditions. It evaluates the strength of adhesive joints, such as those found in flexible printed circuits, microelectronic assemblies, and encapsulation processes. By measuring the force required to separate bonded surfaces, engineers can validate adhesion quality, detect weaknesses in bonding materials, and ensure compliance with industry standards. This method is crucial for maintaining the durability and functionality of components used in demanding applications, such as those operating in high-temperature or high-stress environments, thereby ensuring product longevity and safety.
Construction and Automotive Applications
Peel strength testing is used to ensure the quality and safety of materials used in the construction and automotive industries. In construction, it is extensively used to assess the adhesive capacity of sealants, tapes, and laminated panels applied onto structural materials. Testing ensured that materials could withstand environmental stresses such as temperature variation, moisture, and mechanical loads, which is necessary for the durability and integrity of the building.
Similarly, in the automotive industry, peel strength testing ensures the weakest adhesives are identified in the assembly, including bonding to windshields, bonding of body panels, and bonding of interior components. These tests enable manufacturers to evaluate the ability of glued joints to withstand forces encountered during vehicle operation, including vibration, heat, and dynamic stress. By verifying the adhesive properties of the adhesive, peel strength testing enhances safety, reduces material failure, and improves product durability in automotive and construction applications that require rigorous testing.
Implementing Effective Peel Strength Testing Strategies
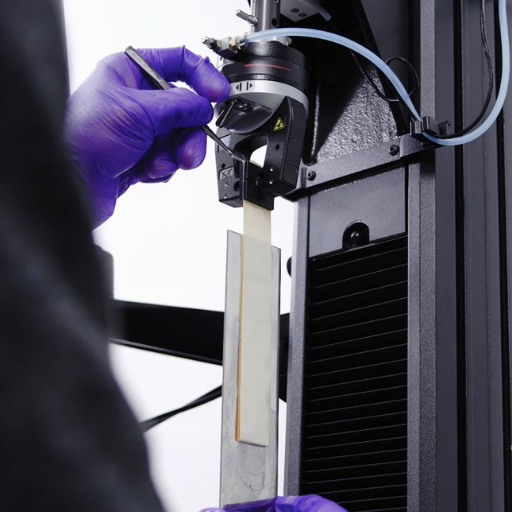

In establishing an optimal strategy for peel strength testing, many technical parameters must be considered. The appropriate test method must be chosen (e.g., T-peel, 90-degree peel, or 180-degree peel) considering the application requirements to produce accurate results. Test specimens must be prepared in such a way to properly represent the real-world conditions (dimensions, surface cleanliness, adhesive application). Establishing standard test procedures, such as test environmental conditions, peel rate, and test specifications (e.g., ISO or ASTM), ensures that results will be more repeatable and comparable. A good testing machine that measures force precisely and accurately acquires data, offering the best results. Equipment calibration and technician training should be conducted periodically to ensure all equipment operates reliably.
Tips for Accurate Testing
- Preparation of Specimens: All test specimens must be prepared exactly as described in the standard or guideline; factors such as dimensions of materials, adhesive application, and curing times should have appropriate attention or results can be inconsistent.
- Control Environmental Conditions: To maintain a controlled testing environment, ensure that the levels of temperature and humidity remain constant. Peel strength or adhesive performance is highly influenced by temperature and humidity.
- Calibrate Equipment: To ensure that testing machinery and force measurement devices are regularly calibrated to maintain their accuracy, conforming to the principle of minimizing errors resulting from equipment drift or inaccurate readings.
- Standardize Testing Procedures: To enhance the repeatability of results and ensure comparability of results in other laboratories, standardized testing parameters, such as peel rate, angle of separation, and specimen alignment, should be followed.
- Document Results in Detail: Document or record all relevant test parameters and results in detail and in an orderly manner, taking into account any deviations from standard test procedures. This will allow accurate analysis and wise decisions.
Choosing the Right Test Method for Your Needs
The choice of the correct test method is greatly dependent on a full understanding of one’s material, application, and performance requirements. Start by identifying the specific properties and behaviors you wish to test, such as tensile strength, adhesion, and thermal resistance. Then consider the industry standards (i.e., ASTM, ISO) for compliance and reliability. Compare the advantages, limitations, and level of precision that the potential test methods offer against your test objectives. Another factor is seeing if potential test methods can be carried out within the realm of your practical constraints such as sample availability, equipment availability, and budget. Choosing the correct method will maximize the meaning of your results.
Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensuring compliance with the industry standards, I thoroughly analyze the basic regulations of my discipline, such as ASTM for materials testing or ISO for quality management. I constantly refer to authoritative sources, including technical manuals and publications, for standard implementations of my processes. However, I also emphasize the continual application of training and certification updates due to revisions or new standards. Testing methods, in turn, should be checked for compliance with the required level of accuracy and precision given by standards. Lastly, but certainly not least, I implement documentation procedures to verify the conformity of all processes, enabling subsequent audits and independent assessments.
Reference Sources
-
Standard Test Method for Peel Resistance of Adhesives (T-Type Specimen) – ASTM D1876: This source provides details on the peel resistance of adhesive bonds between flexible adherends.
-
ASTM D1876 Adhesive Peel Strength Testing: A detailed explanation of the ASTM D1876 test method for measuring peel separation strength.
-
D903 Standard Test Method for Peel or Stripping Strength of Adhesive Bonds: This standard outlines procedures for determining the comparative peel or stripping strength of adhesive bonds.
-
Peel Test Procedure as per ISO 8510 and ASTM D1876 – A Detailed Guide: A comprehensive guide covering the peel strength testing process and key elements of ASTM D1876 and ISO 8510 standards.
-
F2258 Standard Test Method for Strength Properties of Tissue Adhesives: This standard provides a means for comparing adhesive strengths, particularly for surgical adhesives or sealants.






