Understanding the resilience of materials under sudden impact stands as one among those important pillars that industries descent into the realm of construction and automotive engineering. The Charpy Impact Test has been the foremost accepted method to measure the toughness of material as it orients toward assessing resistance to sudden shocks. This blog shall unearth the ISO standards that govern impact testing and offer uniformity in the regard for technical precision across worldwide applications. Whether an engineer, a researcher, or simply interested in materials testing, the detailed guide shall put clarity upon the importance of the Charpy Impact Test, the important considerations of ISO compliance, and what they entail in actual practice. Stay with us as we dissect the science and standards of one really important engineering tool.
Introduction to Impact Testing
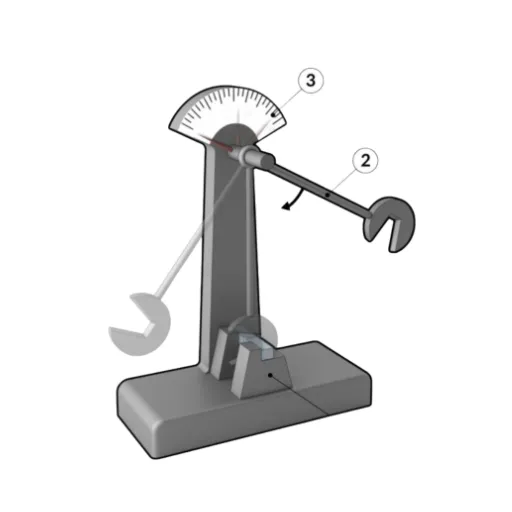
What is Impact Testing?
Impact testing is a technique for assessing materials’ toughness and energy absorption when subject to a sudden force or impact. The information it provides is crucial for describing how a material behaves under dynamic loading conditions and, therefore, if it is suitable for applications subject to such stresses. The test can provide an indication of weak points or regions of brittleness in a material when tested with controlled impact forces.
One thing that an impact test mostly measures is the ability of the material to resist fracturing upon high-speed loading. This is important because, in real life, products and structures are subject to sudden impacts, such as collisions or drops, and these could cause failure if the material is not strong enough. In this way, an impact test proves that the material can resist such conditions to keep its integrity and safety.
Such testing infuses confidence in industries and engineering where material withstands demanding conditions, like civil or automotive industries or aerospace, which are all subject to acute durability under conditions of impact.
Importance of Impact Testing in Quality Assurance
It plays an essential role in quality assurance. Thus, it ensures that materials and products are able to perform under stress and adverse conditions with reliability. These tests measure how much energy a material can absorb in case of an impact, indicating its toughness, brittleness, or resilience. Such information is necessary in determining whether a material is safe and suitable for the intended application.
Laying heavy reliance on impact testing are sectors such as civil construction, automobile manufacturing, and aerospace, which need to adhere to thorough safety and performance standards. For example, in automotive manufacturing, materials should be able to absorb the impact of high-velocity collisions for the protection of vehicle occupants. Furthermore, in construction, structural components should resist sudden forces such as forceful winds or falling debris.
Key Benefits of Impact Testing:
- Identifies potential weaknesses before costly failures occur
- Ensures regulatory compliance across industries
- Builds consumer trust through enhanced product reliability
- Enables manufacturers to fine-tune designs and enhance durability
Overview of Charpy Impact Test
The Charpy Impact Test, being international, determines a material’s toughness through measuring the energy absorbed during fracture. It is a test that subjects a notched specimen to a heavy pendulum blow while gauging the energy absorbed by the breaking of the material. In essence, it acts as a window into the susceptibility of a material to sudden stress or impact.
This test usually entails preparing and machining a standardized specimen, including a notch, cementing or clamping the specimen in the test machine’s holder, and finally actuating the machine so that the pendulum attempts to break the specimen. The machine records the energy absorbed by the specimen during the break. The higher the energy absorption, the tougher the specimen is considered to be, or the resistance to brittle failure.
Standards Governing the Charpy Impact Test
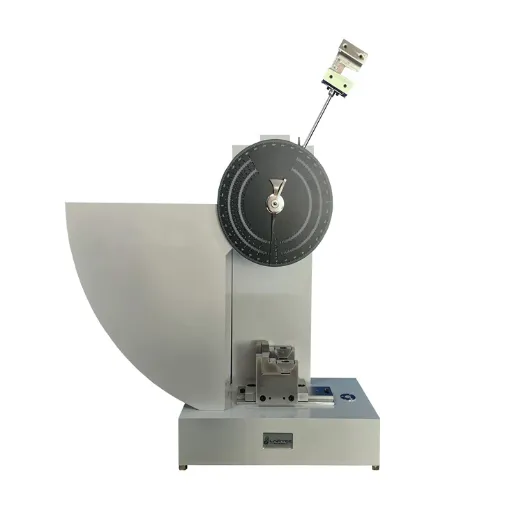

ISO Standards for Impact Testing
The ISO standards for impact testing offer a systematic structure that ensures test results’ accuracy, reliability, and consistency across industries. One such standard is ISO 148-1, which plays a most important role in the series by setting out the Charpy impact test procedures for metallic materials. It prescribes specimen sizes and preparation to be used in the testing and the actual conditions of performing the test so that the test results are uniform across the world.
Key ISO Standards:
- ISO 148-1: Charpy impact test procedures for metallic materials
- ISO 148-2: Verification and calibration of pendulum impact testing machines
- ISO 148-3: Calibration methods for standard test specimens
Another important standard is ISO 148-2, which stipulates the procedures for verifying and calibrating pendulum impact testing machines. If the machines are verified under this standard, their functioning would be kept accurate and reliable so that there is never any discrepancy in the measurement. Along with this, ISO 148-3 describes the calibration methods for standard test specimens, thereby providing further assurance to the integrity of the testing process.
ASTM Standards and Their Relevance
ASTM standards act as multiplies of truthful assurance that do interplay with industries, for consistency’s sake, reliability, and safety types, the standards set guidelines for testing, manufacturing, and quality control of materials to allow any organization to abide by the accepted performance requirement. The product quality is thus improved with ASTM standards, any existing or apparent risk is minimized, regulatory requirements are fulfilled, and, in return, consumer confidence is enhanced.
Application as an example would be a few material tests in ASTM standards. They dictate the testing of materials for their strength and durability and impact-resistance, cryogenic or even any temperature performances. They apply tests in construction, automobile and manufacturing, where failure of material would lead to serious construction and safety concerns. Hence ASTM standards endorse engineers and scientists to arrive at a conclusion that is trustworthy about whether the material fits the application for the said uses.
Key Differences Between ISO and ASTM Standards
| Aspect | ISO Standards | ASTM Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | International organization with global consensus model | Originally constituted in the United States with global reach |
| Scope | More general framework for global compliance | More detailed and technical, industry-specific focus |
| Application | Referenced by governments for policy development | Used for precision in manufacturing and engineering processes |
| Participation | National standard bodies worldwide participate | Voluntary member participation from technical industries |
Types of Impact Testing
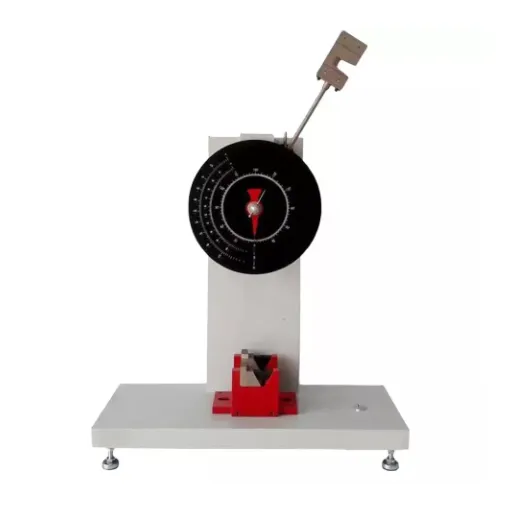

Charpy vs. Izod Impact Tests
The Charpy and Izod assays are two test methods that actually measure materials’ toughness-through being resistant to impact. Both tests try to establish the behavior of an object under sudden force, but they differ concretely in their mode of operation and applications.
The primary difference between the two is in the holding of the specimen. The Charpy test horizontally places the sample in such a manner that the specimen will be hit in the middle on the unsupported section. On the other hand, the Izod test holds the specimen in a vertical position so it can be struck near the top of the specimen. The difference in specimen orientation results in differences in impact energy dispersion and absorption through the material.
Overview of Notched Bar Impact Testing
Notched bar impact testing is performed to ascertain the toughness and fracture behavior of materials at high strain rates. For assessing materials’ behavior under sudden impact and for gaining insights into their potential for energy absorption and fracture resistance, this particular test is appropriate. This method turns out to be almost imperative for the identification of materials that will function well under demanding conditions, such as extreme weather or dynamic loading.
The test generally consists of striking a notched specimen by a pendulum or hammer to impose stress at the notch site, simulating a concentrated load. The two most common types of notched bar impact tests are Charpy and Izod, with differences arising from the orientation of the notch and how the specimen is mounted.
Multiaxial Impact Testing Explained
Multiaxial impact testing method tests materials reacting to forces under simultaneous actions in multiple directions. Traditional impact test measures resistance with respect to a force acting in one direction only; however, this procedure simulates real-life conditions where complex stresses act on the materials. It analyses how a material behaves in respect of durability and strength when subjected to multidirectional loads, aiding industry better in performance appraisal.
In this test, some controlled forces are applied on the material at various angles or axes. For instance, such a test can simulate a collision, dynamic vibration, or a sudden change in pressure, all of which are scenarios commonly encountered in automobile, aerospace, and construction applications.
Recent Updates in Impact Testing Standards

Changes in ISO 148-1 and Their Implications
This standard, which specifies requirements for Charpy impact testing of metallic materials, has been amended recently to improve the accuracy and reliability of testing results. One of the more prominent revisions involved a tightening of dimensions allowed for test specimens and their respective tolerances. This enforces consistent methods for sample preparation and minimizes any variation that may arise during testing.
A further change involves the calibration guidelines for impact machines. With the calibration of equipment required, this ISO specification emphasizes that impact equipment must absorb energy correctly and hence provide accurate measurements. These changes were introduced in order to enhance the consistency of results between disparate testing entities, increasing confidence in the reliability of the data presented.
Implications for Industry:
- Manufacturers: Must change sample preparation methods and equipment calibration practices
- Testing Laboratories: Greater emphasis on procedural accuracies and machinery maintenance
- Quality Standards: Enhanced confidence in material performance determinations
Impact of New ASTM Standards on Testing Protocols
The new ASTM standards are set to introduce further reliability and uniformity in testing protocols so that better outcomes can be attained in material analysis. This impact, among others, includes the arising necessity for accuracy in the preparation of samples, etc. The standardization of those methods will greatly aid in comparing results from different laboratories, thus reducing variance and enhancing confidence in testing outcomes.
How Businesses Can Adapt to Changes in Standards
- Stay Informed: Subscribe to technical publications, attend industry seminars, or participate actively in professional associations
- Equipment Review: Conduct thorough procedural and equipment reviews to implement changes consistent with modified standards
- Staff Training: Invest in comprehensive training programs for employees to execute updated methods correctly
- Quality Control: Set up daily compliance mechanisms through regular audits and accredited laboratory testing
Challenges in Impact Testing

Common Equipment Limitations
Calibration inconsistencies form a major equipment limitation in Charpy impact testing. Given a testing machine that has not been calibrated regularly to ISO standards, the results obtained can be rendered unreliable or invalid. Regular calibration ensures that measurement of energy absorption is consistent with the actual level of energy absorption at the thresholds required by the standards.
Critical Issues to Monitor:
- Wear and tear of crucial components (pendulum, anvils)
- Environmental condition variations (temperature changes)
- Mechanical irregularities affecting specimen alignment
Interpreting Test Results Accurately
Accuracy and consistency should be maintained during the interpretation of Charpy impact test results through the ISO standards. The Charpy impact test examines the relative energy absorption by the specimen under fracture. This energy absorption indicates the toughness of the material under test conditions. The ISO standards, therefore, lay detailed prescriptions so that results can be expected to remain consistent and reliable under various circumstances of testing.
ISO standards emphasize the control of several variables like specimen size, notch geometry, and test temperature. All these can make huge changes in the result of the test. Specimens must have dimensions as specified in the ISO standard, as a deviation, even if minute, may lead to incorrect test results.
Addressing Variability in Test Data
A variation in the Charpy test data needs to be taken into consideration when carrying out Charpy impact testing following ISO standards. This test measures in general the energy spent by the fracture of the specimen, which gives an idea about the toughness of the material and suitability for certain applications. Variations could set in owing to specimen preparation, equipment calibration differences, or environmental conditions during testing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the standards for impact testing?
A: Standards for impact testing comprise the various methods and protocols given by ASTM, ISO, and other standards bodies. These standards describe how to determine the impact resistance of materials, chiefly plastics and metals, so that test results are uniform and reliable.i
Q: What different in Charpy and Izod test?
A: Both Charpy and Izod tests are impact tests applied to determine the strength of materials. In the Charpy test, a notched specimen is hit by a swinging pendulum, and in the Izod test, the specimen is held vertically in a vice for the strike. Both methods have their special application and serve for different materials.
Q: How are plastic materials evaluated by the process of impact testing?
A: Impact testing constitutes the assessment of plastic materials in their resistance against a sudden strike or impact. This knowledge will be of use while choosing suitable plastic for almost any environment where it may confront an impact condition.
Q: What conditions are set forth for ASTM E23?
A: Conditions for ASTM E23 specify how to prepare a specimen and at what temperature to conduct the test and the direction of impact; thus these give validity to the obtained results and enable comparison between results obtained with various testing systems.
Q: On what kinds of materials are impact tests generally performed?
A: Impact test methods are generally applied to plastics, structural steel, and other metallic materials. They exercise the impact properties and the toughness characteristics of these materials bearing on the application of these materials in industry.
Q: What is the significance of the Izod impact strength test?
A: The Izod impact strength test measures the energy absorbed during the impact on a vented specimen. This test is significant since it defines the impact toughness of materials. In the case where applications see materials subjected to sudden forces, the testing becomes very mandatory.
Q: How differ impact testing systems from standard testing machines?
A: Impact testing systems have basically been conceived and applied to measure the response of materials to impact forces. Compared to the ordinary testing machines that may perform the variety of mechanical tests, the impact testing systems are just used to check the impact resistance and toughness of materials.
Q: How verification of Charpy results determine the testing of materials?
A: Verification of Charpy results is critical in material testing so as to truly verify the accuracy and reliability of the impact test data. By confirming the test results, manufacturers and engineers can be sure that the material will behave as expected under actual conditions.
Q: Tell me about impact testing on different materials.
A: Impact testing requirements vary for different materials depending on the expected use. For example, plastics have standards different from those for metals. Moreover, the materials must be subjected to known impact test methods that conform with their particular properties and to the standard requirements of the industry using them.
References
-
Understanding Different Impact Tests Using ASTM & ISO Standards – This resource explains various impact tests and their standards.
-
Impact Testing by Instron – Covers traditional standards like the Charpy pendulum impact test (ISO 179/ASTM D6110) and the Izod test (ISO 180/ASTM D256).
-
Most Common Standards for Impact Testing – Discusses widely accepted standards for Charpy, Izod, and drop weight impact testing.
-
Charpy Machine Verification Program by NIST – Details the NIST program for verifying Charpy machines and ensuring quality in steel products.







